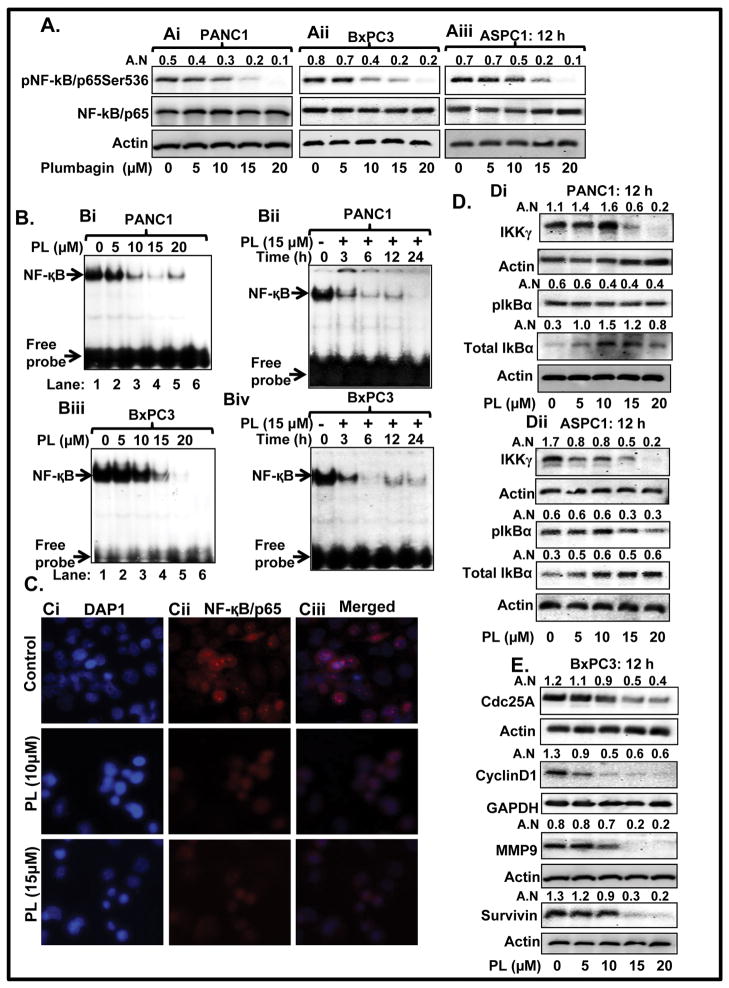
Figure 3. PL inhibits activation of NF-κB in PC cells.
A. Expression level of pNF-κB/p65Ser536 and total NF-κB/p65 in PANC1 (Ai) BxPC3 (Aii) and ASPC1 (Aiii) cells as determined by Western blot analysis. B. EMSA assays represent dose and time-dependent effect of PL on DNA binding activity of NF-κB in PANC1 (Bi–Bii) and BxPC3 (Biii–Biv) cells. Lane 6 of Bi and Biii EMSA blot represent mutant consensus sequence of NF-κB. C. Localization of NF-κB/p65 in PANC1 cells as determined by immunocytochemistry. Representing pictures illustrating DAPI (Ci), NF-κB/p65 (Cii) staining and merged images of DAPI and NF-κB/p65 (Ciii) in control (upper panel) and PL treated cells (Lower panel). D. Effect of PL on protein levels of IKKγ, pIkBα, and total IkBα in PANC1 (Di) and ASPC1 (Dii) cells as determined by Western blot analysis. (E) Expression levels of Cdc25A, Cyclin D1, MMP9, and survivin as determined by Western blot analysis.