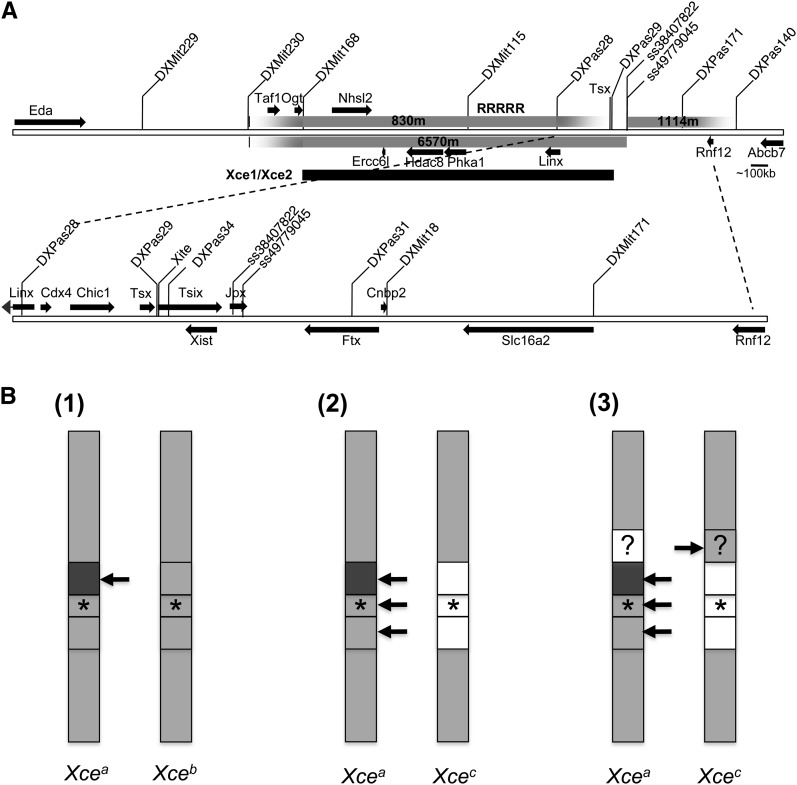
Figure 5.
Xce regions and models. (A) Map of breakpoints for RX2 derived 830m, 6570m, and 1114m X chromosomes. Below is the Xce candidate region (Xce1/Xce2) that overlaps the region mapped by Simmler et al. (1993) and Chadwick et al. (2006). (See RX2 chromosomes and Xce1 and Xce2 in Table S1.) Relative location of genes (arrows) and genetic markers is extrapolated from UCSC Genome Browser on Mouse July 2007 (NCBI37/mm9) Assembly. On the upper extended view, only genes >10 kb are indicated within the 830m X chromosome region; RRRRR designates the location of a highly repetitive sequence. Expanded view of X chromosome region between DXPas28 and Rnf12 is shown below. (B) Regions along the X chromosome that may be responsible for the Xce effect are demarcated in females heterozygous for Xcea and Xceb (B(1)) and heterozygous for Xcea and Xcec (B(2) and (3)) chromosomes. Regions are shaded differently where sequence is contributing to the Xce effect; the darker the shade the more likely the chromosome is chosen to be inactivated. The arrows point to the X most likely chosen to be inactive when the corresponding region is heterozygous. The Xist/Tsix locus is designated by ★. The proximal boundary of Xist/Tsix is between DXPas28 and DXPas29 and the distal boundary is between Xist and DXPas31. Boundaries of demarcated regions proximal and distal to ★ are inferred from Simmler et al. (1993) in (B(1)) and our data in (B(2)) and (B(3)). (B(1)) Based on Simmler et al., the Xce effect in females with an Xcea and Xceb chromosome is due to differences in sequence proximal to DXPas29 and within sequence spanning DXPas28 and Eda. Based on the overlapping Xce candidate region Chadwick et al. (2006) identified, this candidate Xce region may further be reduced to sequences within DXMit168 and DXPas29 (B(2)). Our data suggest that at least three discrete loci on the X chromosome that may contribute to the Xce effect in females with an Xcea and Xcec chromosome. Our analysis indicates that Xcec Xist/Tsix spanning sequence (★) contributes to the Xce effect. The minimal Xce region proximal to Xist/Tsix is defined by the RX2 830m X chromosome 129S1 sequence spanning DXMit168 and DXpas28. The minimal Xce region distal to ★ is defined by the RX2 1114m chromosome with 129S1 sequence spanning ss49779045 and DXMit171. (B(3)) As depicted by the corresponding regions (open) on the Xcea chromosome and (shaded) on Xcec chromosome, if multiple X chromosome Xce loci contribute to the Xce effect, then perhaps one locus promotes preferential inactivation the Xcec chromosome.