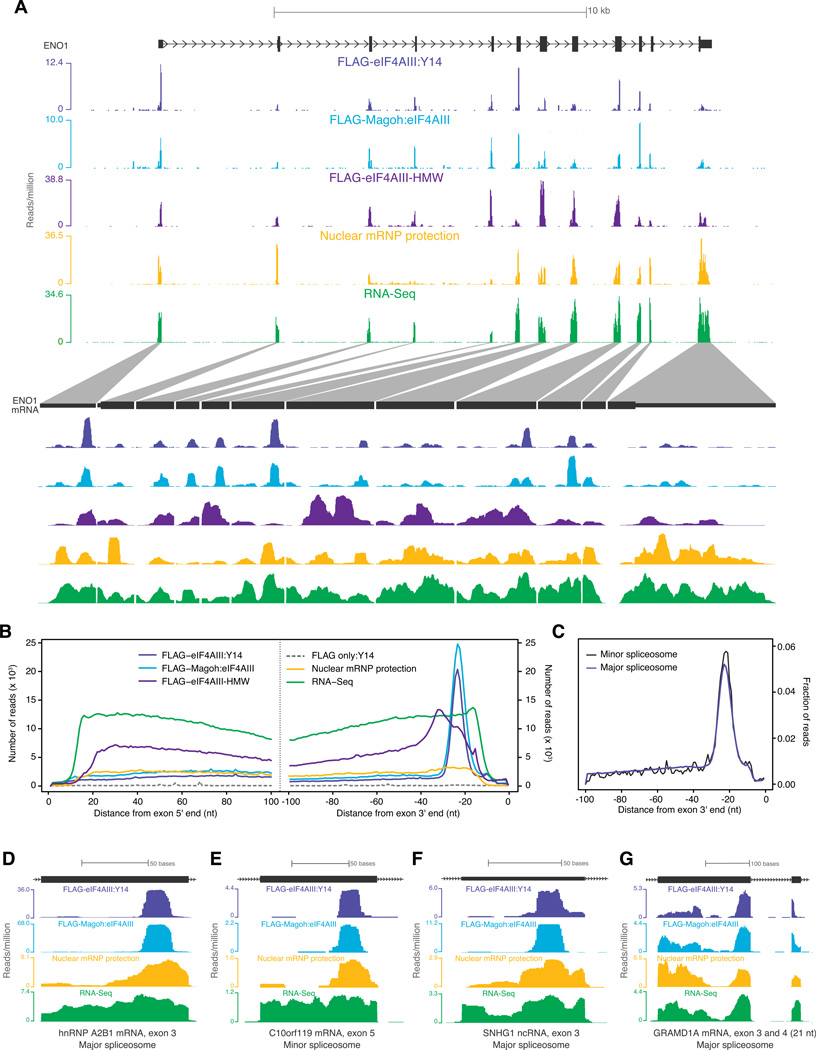
Figure 3. EJC occupancy on endogenous mRNAs.
A. Distribution of short EJC footprints (FLAG-eIF4AIII:Y14 and FLAG-Magoh:eIF4AIII), HMW EJC footprints (FLAG-eIF4AIII-HMW), nuclear mRNP footprints or RNA-Seq reads on a representative gene (top half), ENO1, and its spliced mRNA (bottom half). Scale is indicated at top; reads per million at the highest position within each library window are indicated at left.
B. Meta-exon analysis of read distribution. Composite plots of distances from the centers of all exon-mapping reads to the 5′ (left panel) or 3′ end (right panel) of each read's parent exon for the indicated libraries.
C. Meta-analysis of exons upstream of major or minor spliceosome introns. Composite plots for FLAG-Magoh:eIF4AIII library reads mapping to exons upstream of introns excised by the “major” (~1.7×105 introns) or “minor” (427 introns) spliceosome. In both plots, the fraction of reads at each nucleotide position out of all reads within 100 nt from exon 3′ end was plotted.
D-G. Profiles of short EJC footprints, nuclear mRNP footprints and RNA-Seq reads (as in A) on individual exons. Distinguishing features of each exon are indicated at bottom.
See also Figure S3.