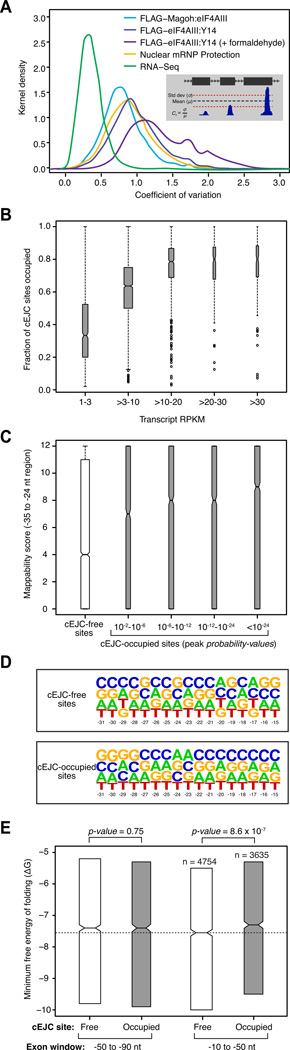
Figure 4. Variability in cEJC occupancy and contributing factors.
A. Signal variability among cEJC sites on individual mRNAs. Smoothed histograms of coefficient of variation (Cv) in the number of reads at each cEJC site (−15 to −31 nts from exon junctions) within a single transcript in a set of 4366 highly expressed transcripts. Inset: parameters used to calculate Cv.
B. Fractions of occupied cEJC sites per transcript. Included were all mRNAs with >10 introns and representative transcript RPKM >1. All cEJC sites with a significant peak (probability-value < 0.01) overlapping the −24 position in the FLAG-Magoh:eIF4AIII set were considered occupied. The box-plots show the interquartile range (IQR) of fraction occupied cEJC sites in each RPKM bin. The whiskers are drawn at 1.5 times the IQR and outliers are shown as open circles. Median (black horizontal line) and its confidence interval (notch) are also indicated within each box-plot.
C. Range of mappability scores at cEJC-free (white) and cEJC-occupied (gray) sites from all spliced transcripts with RPKM >10. Occupied sites were binned by peak significance (probability-values). Box-plots are as in B.
D. Nucleotide frequency plot at cEJC-free and -occupied sites. All sites with mappability score ≥8 from all spliced transcripts with RPKM >10 were used.
E. Interquartile range of the minimal free energy of folding for two different 40 nt exonic windows (−50 to −90 nt from exon junctions, left; −10 to −50 nt from exon junctions, right) for cEJC-free (white) and cEJC-occupied (gray) sites from D except that included cEJC-occupied sites had a peak probability-value <10−12. The total number of sites in each dataset is indicated. Box-plots are as in B except only the IQR is shown. The dashed line accentuates statistically significant (indicated by non-overlapping notches) difference in median minimal free energy of cEJC-free and -occupied sites.
See also Figure S4.