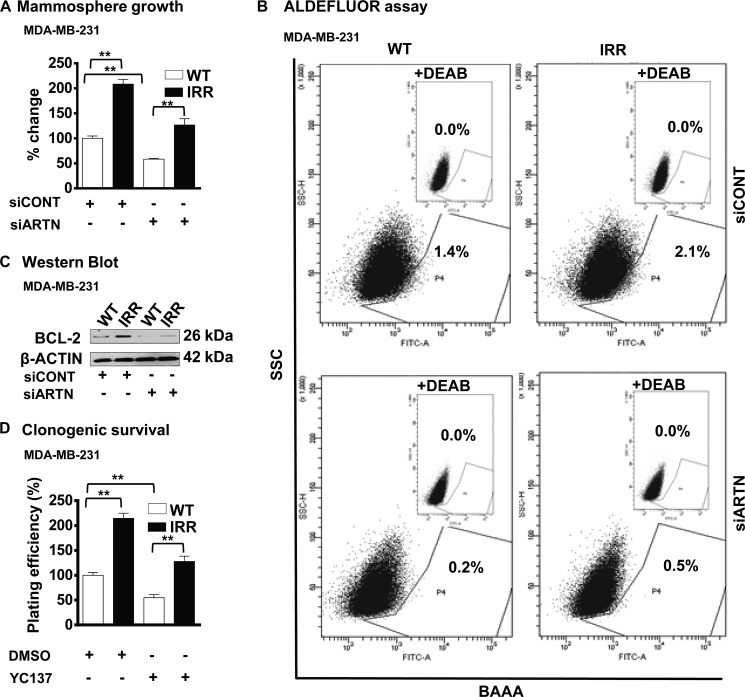
FIGURE 7.
BCL-2 is downstream of ARTN mediated acquired resistance to ionizing radiation and the increased CSC-like population in ER-MC cells. A, MDA-MB-231-WT and -IRR cells were seeded in ultra low attachment plates in mammospheric growth media ± siRNA to ARTN. After 10 days, growth was measured by alamarBlue. Mammosphere formation by MDA-MB-231 IRR cells was increased as compared with respective WT cells. Depletion of ARTN by siARTN significantly decreased mammosphere formation in both IRR and WT cells of MDA-MB-231. B, ARTN-mediated acquired resistance to ionizing radiation resulted in an increased CSC-like population in ER-MC cells. Cells were incubated with Aldefluor substrate (BAAA, BODIPY®-aminoacetaldehyde) to define the Aldefluor-positive, and a specific inhibitor of ALDH1, diethylaminobenzaldehyde (DEAB), was used to establish the base-line fluorescence. Flow cytometry plots indicate side scatter (SSC) versus fluorescence intensity. The ALDH1+ cell population in MDA-MB-231 IRR cells was increased as compared with WT cells. Depletion of ARTN by siARTN significantly decreased the ALDH1+ cell population in IRR and WT cells of MDA-MB-231. C, Western blot was used to determine BCL-2 protein levels in MDA-MB-231-WT and -IRR ±siRNA to ARTN. β-Actin was used as the loading control for cell lysates. The sizes of the detected protein bands in kDa are shown on the right. D, clonogenic survival is shown. MDA-MB-231-WT and -IRR cells± YC137 were exposed to a 4-Gy dose of IR, and 24 h later, 600 cells/well were seeded in 10% serum-containing media in 6 well plates. After 2 weeks, colonies with greater than 50 cells were counted by crystal violet stain, and plating efficiencies were (number of colonies formed/number of cells seeded × 100. **, p < 0.01.