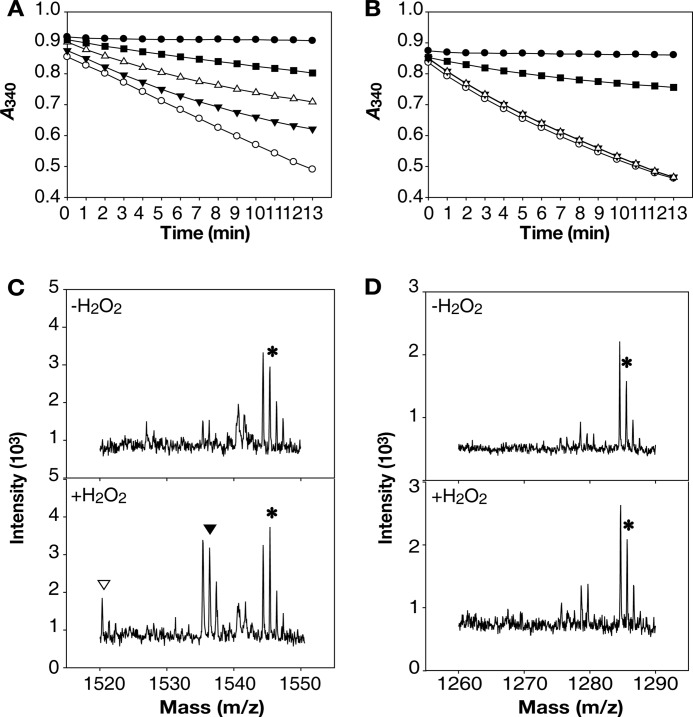
FIGURE 3.
Inactivation and overoxidation of Prxs by H2O2in vitro. A and B, the peroxidase activities of Prx2 (A) and Prx1 (B) were determined by measuring NAD(P)H consumption in the reaction mixtures. A, the reaction mixture contained none (●), TrxA/TrR (■), and TrxA/TrR and Prx2 with various concentrations of H2O2 (0.1 mm H2O2 (○), 1 mm H2O2 (▾), 5 mm H2O2 (▵)) in addition to NADPH. B, the reaction mixture contained none (●), AhpF (■), AhpF and Prx1 with various concentrations of H2O2 (0.1 mm H2O2 (○), 1 mm H2O2 (▾), 5 mm H2O2 (▵)) in addition to NADH. The S.E. were too small to denote by error bars. C and D, Prx2 and Prx1 were reacted (lower panels, +H2O2) or unreacted (upper panels, −H2O2) with 1 mm H2O2, alkylated, digested with AspN, and analyzed using MALDI-TOF-MS. C, mass spectrum of Prx2 peptides. Peptides with CP were indicated; *, m/z = 1545, CP-CH2CONH2; ▾, m/z = 1536, CP-SO3H; ▿, m/z = 1520, CP-SO2H. D, mass spectrum of Prx1 peptides. A peptide with CP was indicated; *, m/z = 1285, CP-CH2CONH2.