Figure 5. .
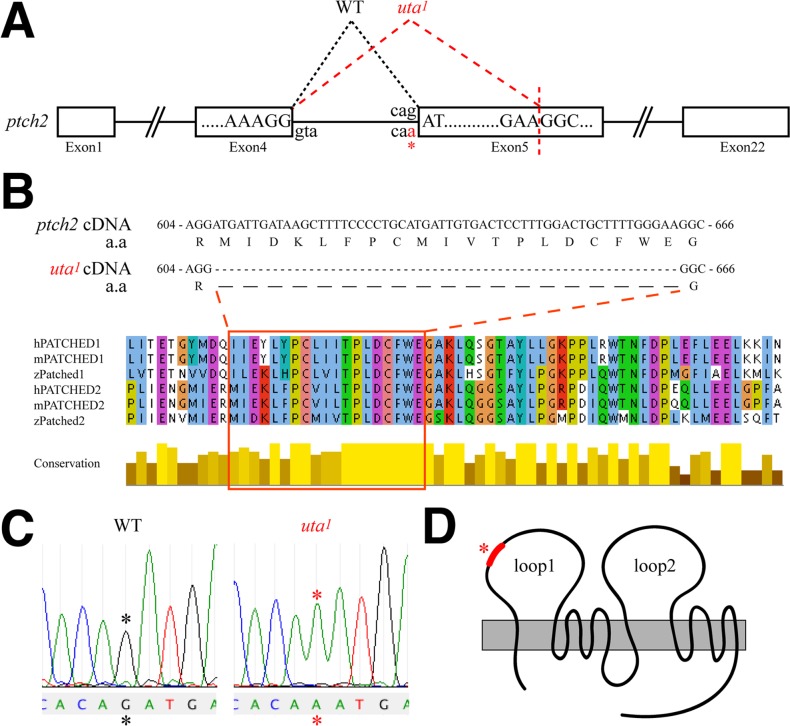
uta1 mutants possess a splice-acceptor site mutation in patched2. (A) Schematic of the ptch2 genomic locus. uta1 mutants possess a G → A mutation at the Intron 4 splice-acceptor site (asterisk), and a cryptic splice site is recognized in exon 5. (B) Mis-splicing of ptch2uta1 results in the excision of 57 bp of ptch2. These excised bases encode 19 amino acids that are highly conserved between ptch1 and ptch2 orthologs in human (h), mouse (m), and zebrafish (z). (C) Genomic sequence traces from wild-type and uta1 mutants indicating the Intron 4 mutation (asterisk). (D) The 19 amino acids absent from ptch2uta1 are predicted to contribute to the first extracellular loop of ptch2 (modified from Briscoe et al.18).