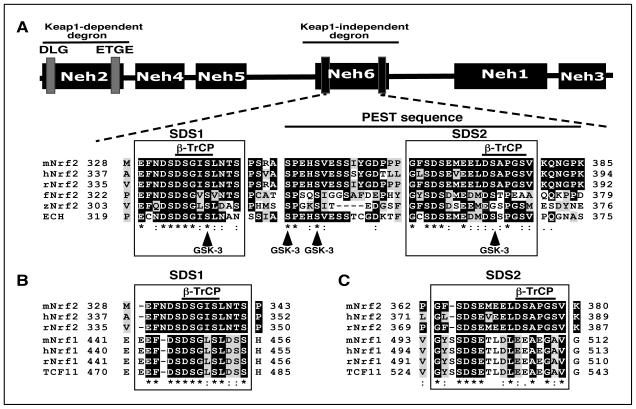
Figure 1.
The Neh6 domain of Nrf2 comprises two conserved regions that include putative β-TrCP binding sites and a potential PEST sequence.
A) Amino acid sequences corresponding to the Neh6 domain of Nrf2 from mouse (m), human (h), rat (r), frog (f), and zebrafish (z), along with that of ECH (i.e. chicken Nrf2) have been aligned using the T-Coffee tool (at http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/tcoffee/). White letters on a black background represent residues that are identical across at least half of the species studied, and black letters on a grey background are conserved residues. The two boxes designated SDS1 and SDS2 contain sequences enriched with Ser and Asp residues. The solid horizontal bar over residues corresponding to 347 and 385 in mouse Nrf2 depicts a potential PEST sequence that is enriched with Pro, Glu, Ser and Thr residues (6). Within the SDS1 and SDS2 boxes, a solid horizonal bar is shown above sequences that represent putative β-TrCP binding sites. The residues that are predicted to be phosphorylated by GSK-3, based on the Scansite program (at http://scansite.mit.edu), are shown at the bottom as vertical arrows.
B) Amino acid sequences of the SDS1 region in the Neh6 domain of mNrf2, hNrf2 and rNrf2 have been aligned with a similar region in the acidic domain-2 of mNrf1, hNrf1, rNrf1 and TCF11, a splice variant of Nrf1 (the protein shown is the human factor).
C) Amino acid sequences of the SDS2 region in the Neh6 domain of mNrf2, hNrf2 and rNrf2 have been aligned with a similar region in the Neh6-like domain of mRn1, hNrf1, rNrf1 and TCF11.