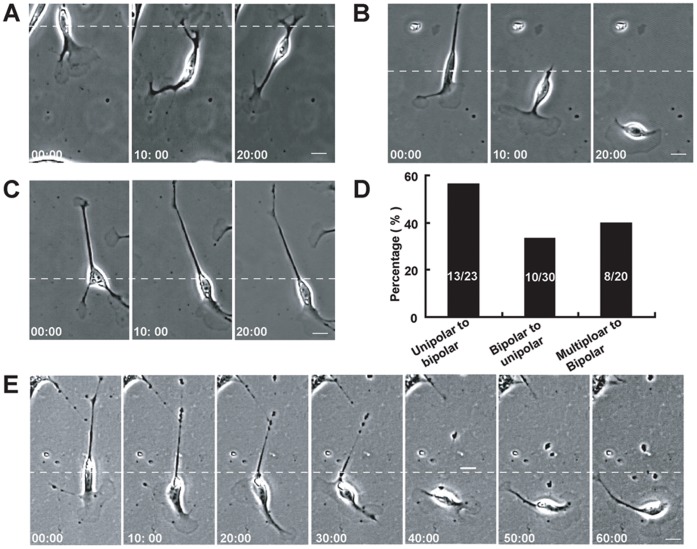
Figure 3. Distinct motile phenotypes of Schwann cells could transform into each other spontaneously.
The example cells were shown in a series of time-lapse images (A–C). (A) A Schwann cell with unipolar morphology gradually transformed into a bipolar phenotype. (B) A Schwann cell with bipolar morphology transformed into a unipolar phenotype. (C) A Schwann cell with multipolar morphology rapidly transformed into a bipolar phenotype. (D) Histogram showing the percentages of transformed Schwann cells in total observed cells. (E) A sample cell showing that one Schwann cell changed its direction of migration through morphological transformation. Time, min, scale bar, 20 µm.