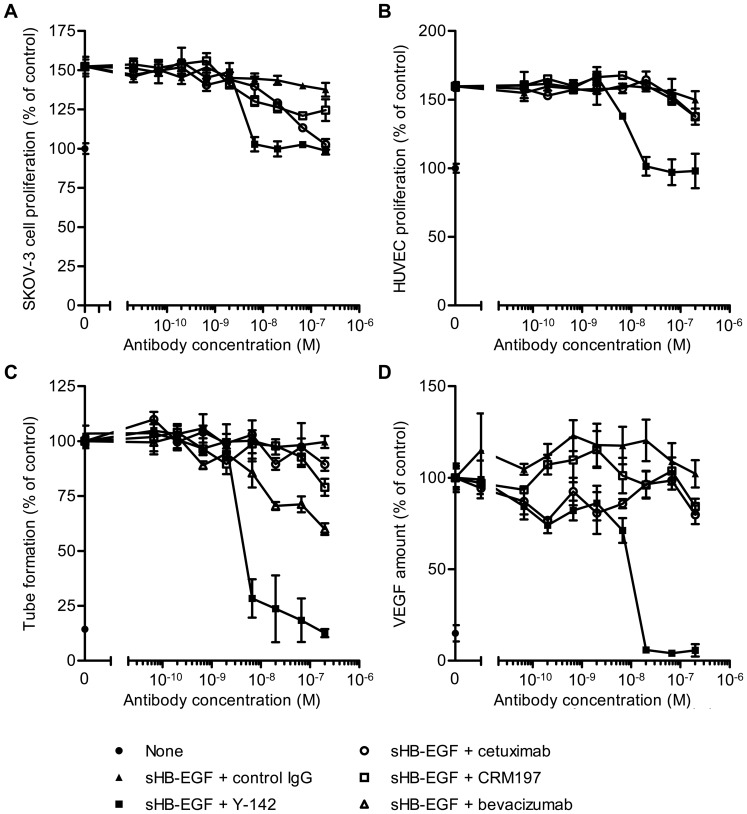
Figure 4. Inhibitory activity of Y-142 against sHB-EGF functions.
(A) and (B) Neutralizing activities of Y-142 against (A) sHB-EGF-induced SK-OV-3 cell proliferation and (B) HUVEC proliferation. SK-OV-3 cells or HUVEC were cultured for 3 days in the presence of sHB-EGF and the indicated concentrations of Y142, cetuximab, or CRM197. Cell proliferation was detected with CellTiter-Glo and calculated as a percentage of the “control” cell proliferation without sHB-EGF. Data points represent the mean ± SD of values acquired in triplicate. (C) Inhibition of HUVEC tube formation by Y-142. HUVEC were cultured on a monolayer of NHDF in the presence of 50 nM sHB-EGF and the indicated concentrations of Y142, cetuximab, CRM197, or bevacizumab for 4 days. HUVEC were then stained with FITC-labeled anti-CD31 antibody. Tube formation (CD31-positive area) was calculated as a percentage of the “control” amount of tube formation in the presence of sHB-EGF. Data points represent the mean ± SD of values acquired in triplicate. (D) Inhibition of VEGF production by Y-142. HUVEC were prepared as in Figure 4C and treated with 50 nM sHB-EGF and the indicated concentrations of Y142, cetuximab, or CRM197 for 4 days. VEGF concentration in the supernatant of co-culture was measured in an electrochemiluminescence-based method. VEGF production was calculated as a percentage of the “control” amount of VEGF produced in the presence of sHB-EGF. Data points represent the mean ± SD of values acquired in triplicate.