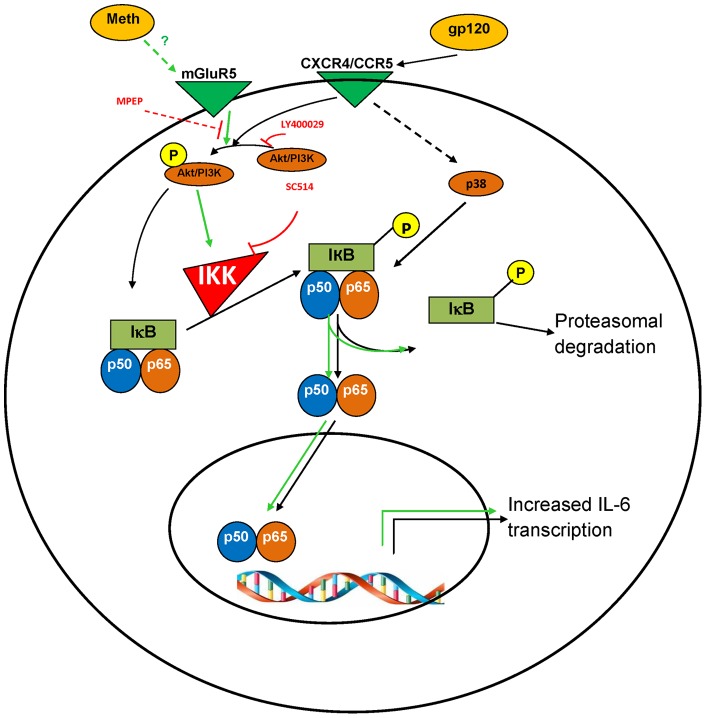
Figure 9. Schematic illustrations of the signaling pathways that mediate the induction of IL-6 by MA and gp120 in astrocytes.
Treatment of astrocytes with gp120 results in the binding of gp120 by the CCR5 or CXCR4 chemokine receptors and the subsequent activation of PI3K/Akt and p38-MAPK. The activation of these two pathways may lead to increased activation of NF-κB. The activated NF-κB then translocates into the nucleus and increases the transcription of IL-6. Treatment of astrocytes with MA results in activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGluR5). The mechanism of mGluR5 activation by MA is unclear, but one possibility is that the increase in extracellular glutamate caused by MA treatment may activate the receptor. mGluR5 then activates the PI3K/Akt pathway [30] which can lead to activation of NF-κB and increased expression of IL-6. Thus, gp120 and MA can induce higher expression levels of IL-6 as compared to the levels observed in the presence of either agent alone.