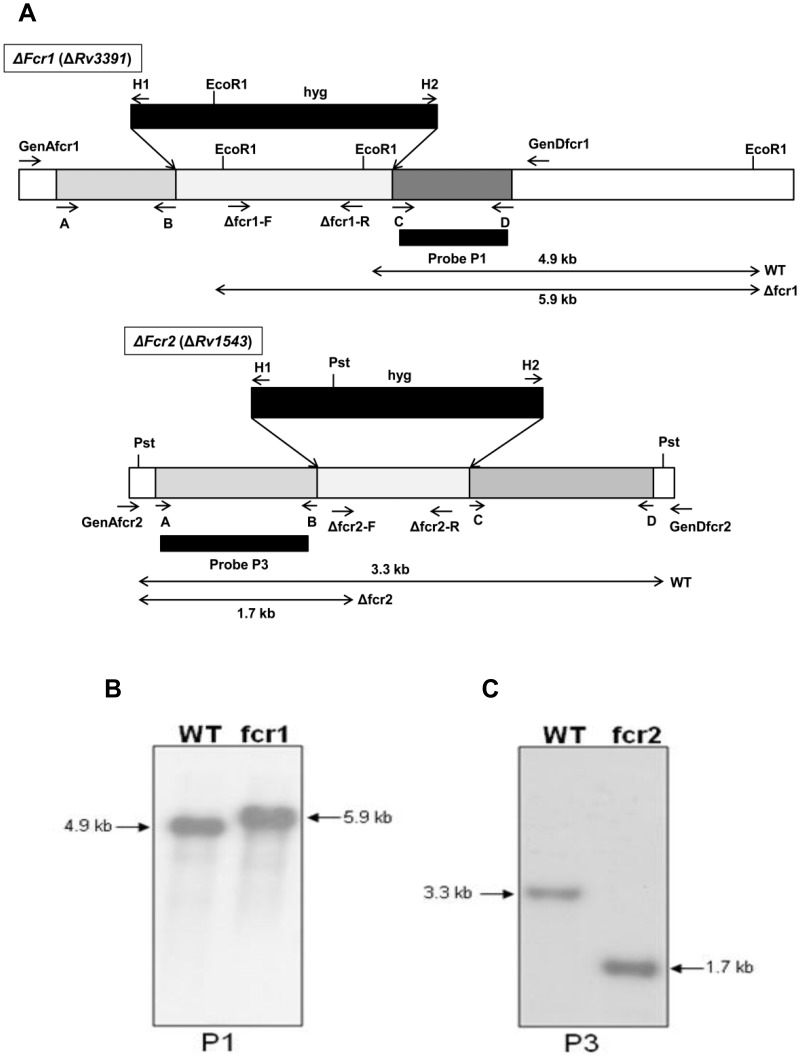
Figure 4. Southern blot analysis of Mtb Δfcr1 and Δfcr2 mutants.
A, Schematic depiction shows the genomic locations of the primers and probes used in the construction and confirmation of fcr deletion mutants. The sequences of the primers are given in Table S1. B, Genomic DNA from WT Mtb and Δfcr1 mutant was digested with EcoRI and hybridized with the 3′-flank of the Δfcr1 construct as probe (P1). The WT fcr1 contains two EcoRI sites in the deleted part of the gene, the last one being only 48 bp upstream of the 3′ flank region of the construct. When this 3′ flank sequence was used as the probe, it hybridized to a 4930 bp fragment of the EcoRI digested genomic DNA (lane WT). When the hyg cassette replaced the native gene sequence, its EcoRI site was situated 1047 bp upstream of the 3′ flank sequence which resulted in a shift of the WT band to 5929 bp (lane fcr1). C, Genomic DNA from WT Mtb and Δfcr2 mutant was digested with PstI and hybridized with the 5′-flank of the Δfcr2 construct as the probe (P3). Wild-type genomic DNA digested with PstI and probed with the 5′ flank of the disruption construct yielded a hybridization fragment of 3292 bp (lane WT). In contrast PstI digested DNA from the mutant strain showed a smaller band of 1741 bp due to the presence of a PstI site in the 5′ region of the hyg cassette (lane fcr2).