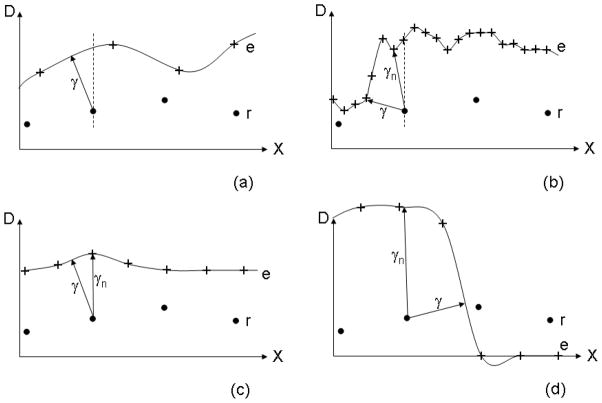
Figure 7.
(a) A nominal example of the reference dose grid (circles), evaluated dose grid (crosses), and cubic interpolation of the evaluated dose (solid line). In this case, numerical methods will determine γ correctly, represented by the length of the arrow, (b) An example where the numerical methods could be distorted by a local minimum (γn) instead of the true γ. (c) A maximum in the evaluated dose that exactly coincides with a reference dose grid position will fail to give the true γ at that grid point, (d) Discontinuities can lead to a failure due to negative dose from the cubic interpolation and local minima.