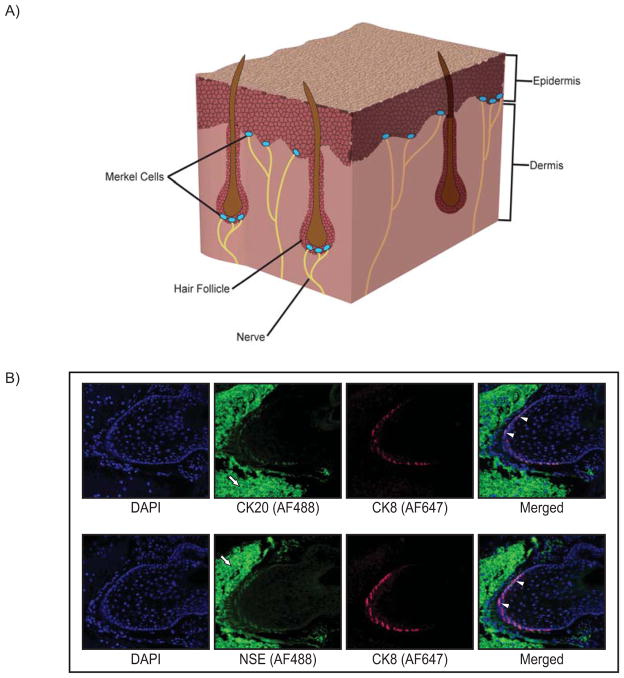
Figure 1. Merkel cell location and immunoreactivity.
A) Cutaneous Merkel cells located in the basal layer of the epidermis associated with the terminal ends of nerves, and also enriched in the bulge region of hair follicles, as depicted in a section of skin tissue. B) Whisker pad tissue was harvested from mice, paraffin-embedded, and representative sections analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence using Merkel cell-specific markers. Top panel: Images of a murine vibrissae follicle co-stained with antibodies specific to the Merkel cell markers cytokeratin 8 (CK8; red Alexa-Fluor 647) and cytokeratin 20 (CK20; green Alexa-Fluor 488). Bottom panel: A vibrissae follicle co-stained with the Merkel cell-specific markers CK8 (red; Alexa-Fluor 647) and neuron-specific enolase (NSE; green Alexa-Fluor 488). In each panel, representative cells staining positive for both Merkel cell markers are indicated with white arrowheads. High background staining with the Alexa-Fluor 488 secondary antibody is evident in cells surrounding the follicle (white arrows). This background staining was also seen in no primary antibody controls (data not shown). Both immunostaining analyses highlight the hair/whisker follicle as a prominent location of Merkel cells.