Table 3.
Scope of Indoles via C-N Bond Formation/1,2-Carbon Shift/Aromatization.[a]
| Entry | Stryryl Anilines | Indole Product | t [h] | Yield [%][b] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
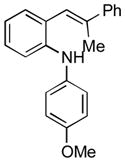 13b |
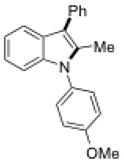 6l |
4.5 | 62 |
| 2 |
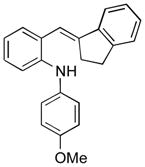 13c |
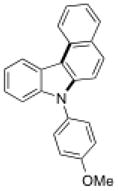 15c |
6 | 52 |
| 3 |
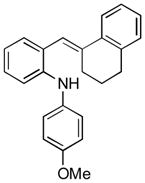 13d |
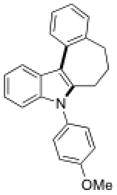 15d |
6 | 60 |
| 4 |
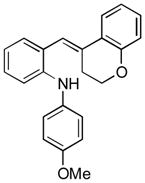 13e |
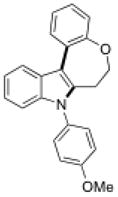 15e |
6 | 58 |
| 5 |
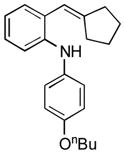 13f |
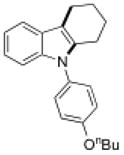 15f |
16 | 40 |
Conditions, unless otherwise noted: 4 mol% Ru(bpz)3(PF6)2, silica gel, air, CH3CN, irradiation with a 18 W LED white light. The newly formed C-N and C-C bonds are shown in bold.
Isolated yields after column chromatography.
Using 6 mol% Ru(bpz)3(PF6)2. Newly formed C-N and C-C bonds are shown in bolds.
