Figure 1. Replicative helicase activation in yeast and humans.
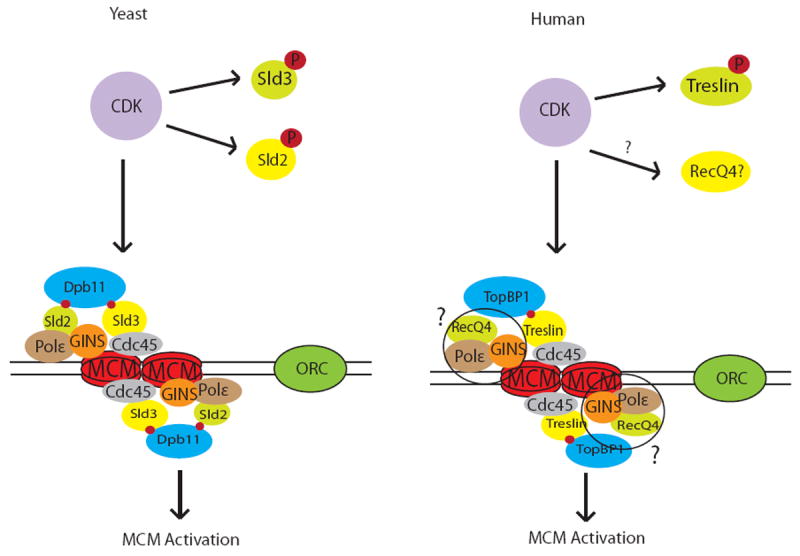
Left: In yeast, CDK phosphorylates Sld2 and Sld3 leading to their interaction with the BRCT repeats of Dpb11 and recruitment of Cdc45, Pol ε and GINS to origin sites to activate the MCM helicase. Right: In humans, CDK phosphorylates Treslin, which then binds TopBP1, leading to recruitment of Cdc45 and activation of the MCM helicase. The Sld2 homologue, RecQ4 does not appear to be regulated by CDK phosphorylation at this time, and its role in recruiting Pol ε and GINS remains unclear (indicated by question marks).
