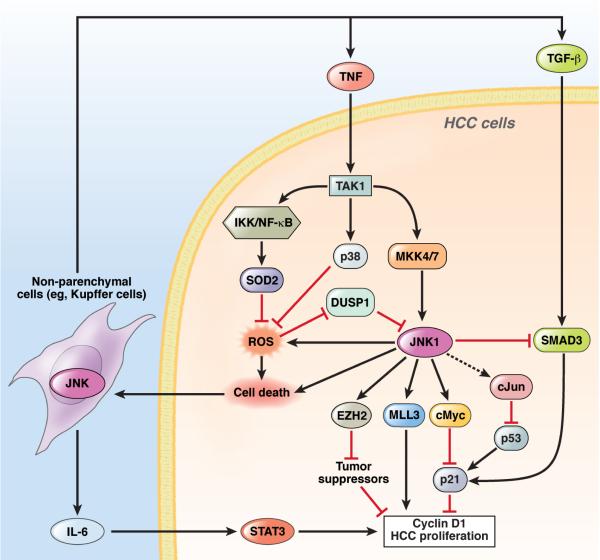
Figure 5. Functions of JNKs in HCC.
In HCC, JNK1 is overactivated either by overactivation of the upstream kinases MKK4 and 7 or the inactivation of DUSP1. Activated JNK1 induces c-Myc, which suppresses p21 expression and promotes HCC proliferation via cyclin D1 expression. JNK1 also upregulates MLL3 and EZH2, 2 histone H3 methyl transferases to increase expression of the cell cycle-associated genes, such as cyclins, and inhibit the transcription of tumor suppressors, respectively. c-Jun inhibits p53 activity post-transcriptionally. JNK1 increase generation of ROS, which is inhibited by p38α and IKKβ activation of NF-κB, through induction of SOD2. JNK1 also inhibits TGF-β–induced Smad3 activation, thereby inducing p21 to suppress HCC promotion. All of these pathways regulate hepatocyte death, which results in the release of IL-6, TNF, and TGF-β through JNK1 in non-parenchymal cells, including Kupffer cells. IL-6 induces HCC proliferation via activation of STAT3in hepatocytes. JNK1 promotes (but TAK1, p38α, and IKKβ activation of NF-κB prevent) hepatocyte death and HCC formation.