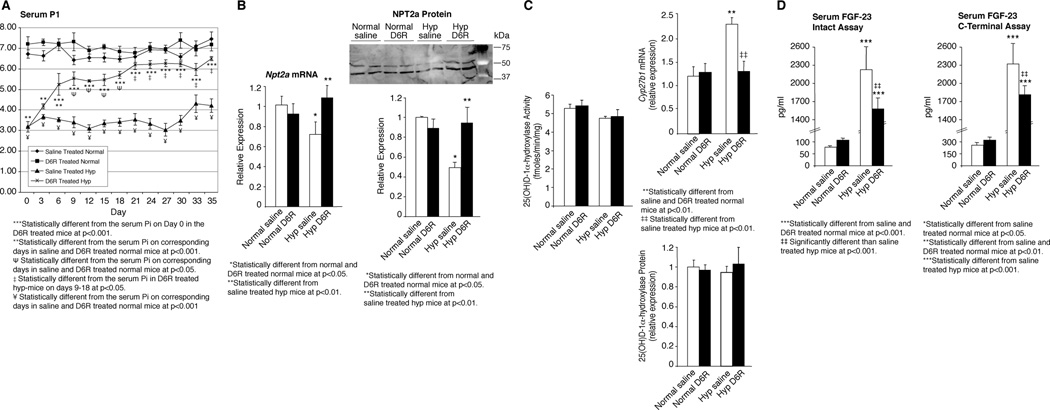
Figure 7. Effects of D6R treatment on phosphate, vitamin D and FGF-23 homeostasis in hyp-mice.
(A) The 5 week D6R treatment course significantly increased the serum phosphorus concentration, compared to baseline, from day 3 through day 35. The increase in the serum phosphorus concentration in the D6R-treated hyp-mice progressed asymptotically, with values from days 3–18 significantly less than those in the saline and D6R-treated normal mice. However, at the asymptotic maximum from days 21–35 of treatment, the serum phosphorus level was significantly greater than those from days 3–18, but more importantly no different than those in the saline- and D6R-treated normal mice. Throughout the treatment period the saline-treated hyp-mice maintained a serum phosphorus concentration significantly less than the D6R-treated hyp-mice and the saline- and D6R-treated normal mice. (B) The normalization of the serum phosphorus concentration in the D6R-treated hyp-mice was accompanied by a significant increase in the Real-time measurements of renal Npt2a mRNA expression at 35 days, to values no different than those in saline- and D6R-treated normal mice. Similarly, the renal NPT2a protein content in the D6R-treated hyp-mice, assessed by Western blots, increased significantly to values no different than in saline- and D6R-treated normal mice. (C) Compared to saline-treated hyp-mice, the D6R-treated mutant mice displayed a significant decrease of the renal Cyp27b1 (25(OH)D-1α-hydroxylase) mRNA expression to values no different than those in saline and D6R-treated normal mice. The unchanging expression of the 25(OH)D-1α-hydroxylase protein and enzyme activity in the D6R-treated hyp-mice indicated that treatment had corrected the abnormal translational regulation of enzyme activity in the mutant mice. (D) Serum FGF-23 levels, measured by an assay specific for the intact molecule and a C-terminal specific assay, was profoundly elevated in the saline-treated hyp-mice. In concert with the normalization of Fgf-23 mRNA (see Figure 5E) and enhanced FGF-23 degradation, D6R treatment of hyp-mice significantly decreased the circulating FGF-23 levels, as measured by both assays. Comparing the data from the two assays, there is a 30% decrease, when using the measurement of intact FGF-23 and only a 24% decrease, when using the C-terminal assa, a difference consistent with an inordinate increase in the circulating C-terminal fragment likely due to a normalization of FGF-23 degradation.