Figure 1.
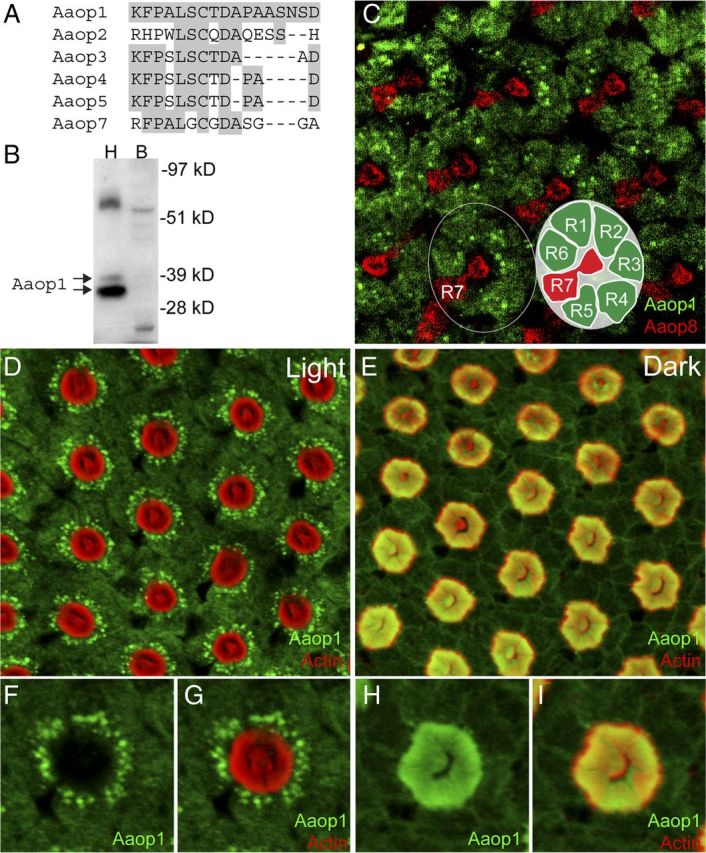
Aaop1 is expressed in Ae. aegypti R1–R6 photoreceptor cells. A, The C-terminal domain sequence of Aaop1 used for production of antisera is compared with the corresponding sequences of other Ae. aegypti long-wavelength rhodopsins. For all sequences, the amino acids identical to the Aaop1 sequence are shaded gray. B, Protein blot analysis shows that the Aaop1 antisera identify two proteins in the 35–37 kDa range in Ae. aegypti head (H) samples (arrows). These proteins are not found in Ae. aegypti bodies (B). C, Confocal image of a distal section to visualize the R7 rhabdomere shows multiple ommatidia in the central region of a light-treated (ZT6–ZT8) retina labeled for Aaop1 (green) and Aaop8 (red). Aaop1 localizes to the R1–R6 photoreceptor cell bodies. Aaop8, but not Aaop1, is expressed in the R7 central cell. The circle encloses a single ommatidium consisting of eight photoreceptors (R1–R8). The inset diagram shows the layout of the R1–R6 and R7 photoreceptors. The R8 photoreceptor lies below the centrally located R7 rhabdomere and is not visible in this image. D, In a light-treated retina at ZT11, Aaop1 (green) displays localization within punctate cytoplasmic structures and is largely absent from the rhabdomeric membranes (actin staining in red). E, In the dark-adapted retina at ZT14, Aaop1 colocalizes with actin within the rhabdomeric membranes. F, G, A single ommatidium from the light-adapted retinal image presented in D is shown for only Aaop1 labeling and for both Aaop1 and actin labeling. Aaop1 is found within punctate cytoplasmic structures and is not detected within the rhabdom area. H, I, A single ommatidium from the dark-adapted retinal image presented in E, is shown for only Aaop1 labeling and for both Aaop1 and actin labeling. Aaop1 is detected within the rhabdom area and not within punctate cytoplasmic structures.
