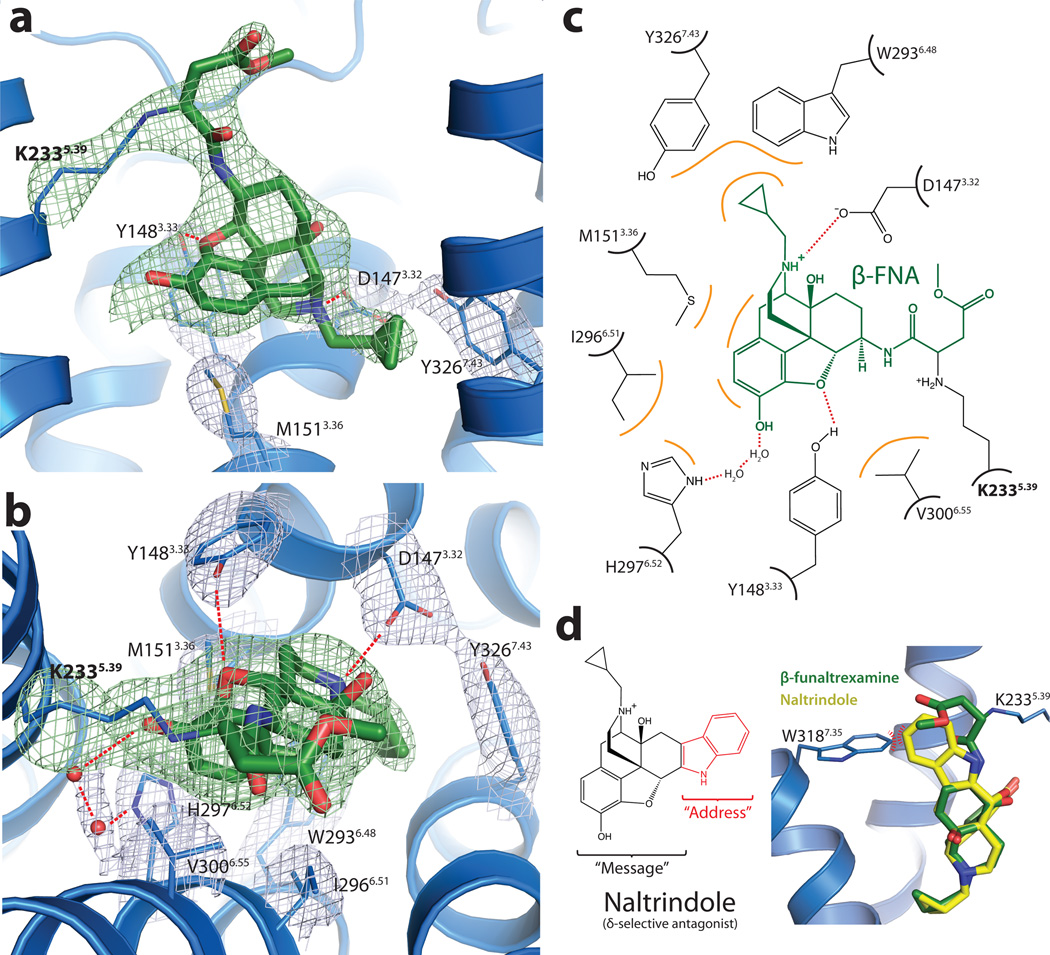
Figure 3. Structural basis for morphinan ligand binding to the μOR.
a, Side view of the ligand binding pocket with polar interactions shown. TM6 is excluded from this view. The electron density used to position interacting side chains is shown in light blue colored mesh depicting the 2Fo-Fc electron density contoured at 1.3 σ. Green mesh depicts an omit map of β-FNA and K2335.39 side chain atoms contoured at 3.0 σ. b, Binding pocket viewed from the extracellular surface. Water molecules are shown as red spheres, with the accompanying electron density shown in light blue mesh. c, The binding site is diagrammed, showing the chemical structure of β-FNA (green) covalently bound to the receptor through K2335.39 (bold). Hydrophobic interactions are shown in orange and polar contacts with red dotted lines. V3006.55 and I2966.51 form extensive hydrophobic contacts with the back face of the ligand (not shown). Two water molecules are positioned between H2976.52 and the phenolic group of β-FNA d, The δOR selective ligand naltrindole includes an indole group that would clash with W3187.35 in μOR, but not with the leucine found in the equivalent position in δOR. The indole has been described as an "address" to target the ligand to δOR, while its efficacy ("message") is determined by the morphinan group on the left 40.