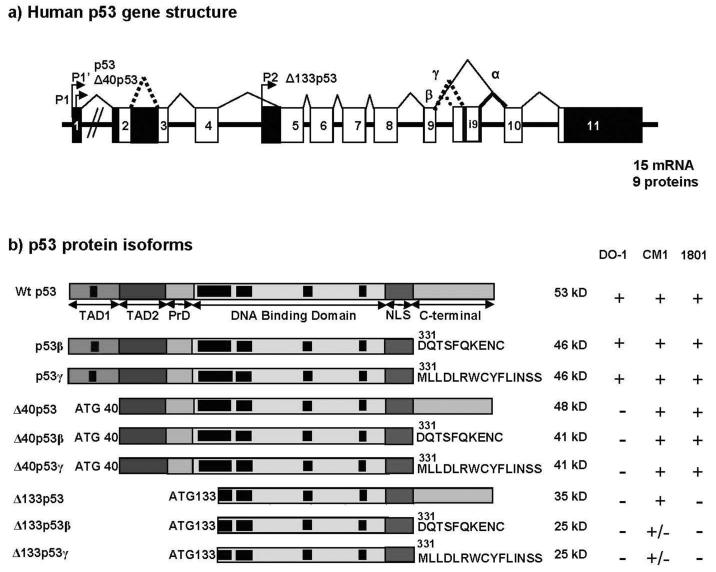
Figure 3. human p53.
a) Schema of the human p53 gene structure: Alternative splicing (α, β, γ) and alternative promoters (P1, P1′ and P2) are indicated.
p53 protein isoforms: p53, p53β and p53γ proteins encoded from P1 or P1′ promoters contain the conserved N-terminal domain (FxxψW) of transactivation (TA). Δ133p53 isoforms encoded from promoter P2 are amino-truncated proteins deleted of the entire transactivation domain and deleted of part of the DNA binding domain. Translation is initiated at ATG-133. Δ40p53 protein isoforms encoded from P1 or P1′ promoters are amino-truncated proteins due to alternative splicing of exon-2 and/or alternative initiation of translation at ATG-40). Δ40p53 protein isoform have lost the conserved N-terminal domain of transactivation (FxxψW) but still contain part of the transactivation domain. Black boxes indicate conserved domains.