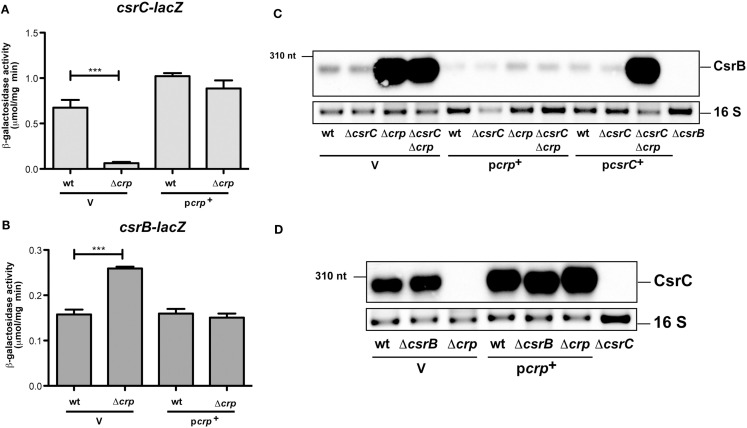
Figure 2.
Analysis of CsrB and CsrC synthesis in the presence and absence of Crp in Y. pseudotuberculosis. The empty vector pAKH85 (V) or its crp+ derivative pAKH37 (pcrp+) were transformed into Y. pseudotuberculosis YPIII and YP89 (Δcrp) harboring a csrC-lacZ fusion (pAKH125) (A) or a csrB-lacZ fusion (pAKH101) (B). The bacteria were grown overnight in LB medium at 25°C. β-Galactosidase activity from overnight cultures was determined and is given in μmol min−1 mg−1 for comparison. The data represent the average ±SD from at least three different experiments each done in duplicate. (C) Expression of CsrB in the presence and absence of Crp and/or CsrC. Total RNA from of Y. pseudotuberculosis wildtype strain YPIII and the mutant strains YP89 (Δcrp), YP126 (ΔcsrC), and YP127 (ΔcrpΔcsrC) harboring the empty vector pAKH85 (V) or the crp-encoding plasmid pAKH37 or csrC-encoding plasmid pAKH59 grown at 25°C were prepared, and analyzed by northern blotting with a CsrB-specific probe. YP69 (ΔcsrB) was used as negative control. (D) Analysis of CsrC production upon overexpression of Crp in the presence or absence of csrB. Total RNA from cultures of Y. pseudotuberculosis wildtype strain YPIII and the mutant strains YP89 (Δcrp), YP69 (ΔcsrB), and YP89 (Δcrp) harboring the empty vector pAKH85 (V) or the crp-encoding plasmid pAKH37 grown at 25°C was prepared, and analyzed by northern blotting with a CsrC-specific probe. YP126 (ΔcsrC) was used as negative control.