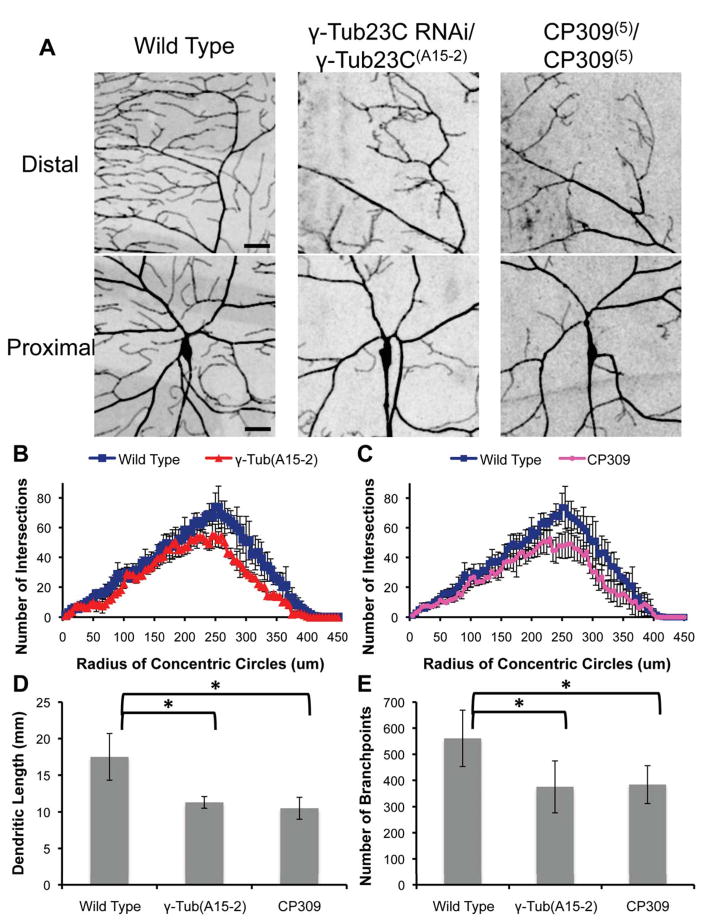
Figure 6. Loss of γ-tubulin or CP309 function alters the dendritic morphology of class IV da neurons.
(A) Dendrite defects in γ-tubulin23C RNAi/γ-tubulin23C(A15-2) and CP309(5)/CP309(5) mutant class IV da neurons, visualized by ppk-cd4-tdtom. Scale bars are 25 μm. (B) and (C) Sholl analysis reveals decreased complexity of the dendritic arbor in the absence of γ-tubulin or CP309. Data are means ± s.d.; n = 4 neurons per genotype. (D) and (E) Total dendrite length and number of branchpoints were reduced in γ-tubulin23C RNAi/γ-tubulin23C(A15-2) and CP309(5)/CP309(5) mutant neurons. Data are means ± s.d.; n = 4 neurons per genotype. Stars indicate P < 0.05.