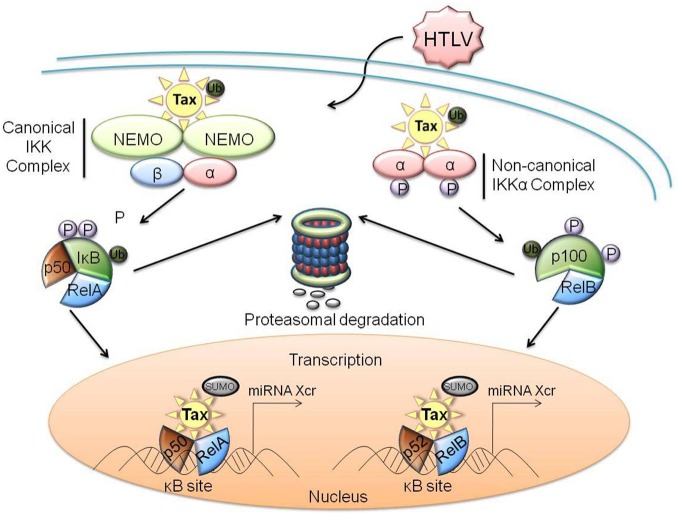
Figure 3.
Protein-protein interactions of HTLV-1 Tax with members of the NF-κB family of transcription factors. Dysregulation of the canonical pathway occurs with the interaction of ubiquitinylated Tax to the cytoplasmic IKK complex, specifically binding to the IKKγ subunit. This interaction results in the phosphorylation of IκB, as well as the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of IκB through the proteasome pathway. RelA is subsequently activated and translocates into the nucleus where SUMOylated Tax recruits RelA to Tax-nuclear bodies, driving Tax-mediated NF-κB transcription. Similarly, ubiquitinylated Tax interacts with the IKKα complex to induce the processing of p100 to p52 within the non-canonical pathway. This promotes the phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and subsequent proteasomal degradation of p100, as well as the recruitment of RelB to the nucleus for activation of Tax-mediated NF-κB transcription. Xcr, transcription.