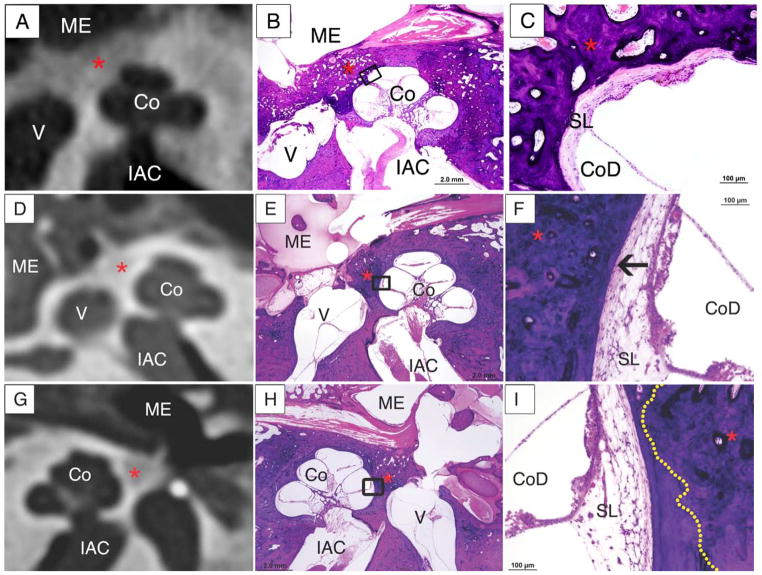
Figure 4.
Evaluation of endosteal margin involvement.
A, B, C: Endosteal margin involvement by otosclerosis (*) is seen on the CT (A), and confirmed on the corresponding histologic slide, shown in low (B) and high (C) magnification. The high power image (C) shows endosteal margin involvment with adjacent spiral ligament hyalinization (arrow).
D,E,F: The CT image (D) fails to demonstrate endosteal margin involvement by the focus of otosclerosis(*). Endosteal margin involvement is seen in the low power (E) and high power (F) photomicrographs of the corresponding histologic slide. In C, an arrow points to hyalinization of the spiral ligament associated with the focus of otosclerosis at the endosteal margin.
G,H,I: The CT image (G) shows absence of endosteal margin involvement, which is confirmed on low (H) and high power (I) photomicrographs. In F, the dotted yellow line represents the border of the focus of otosclerosis, which does not involve the endosteal margin.
Co-cochlea, ME-middle ear, IAC – internal auditory canal, V -vestibule