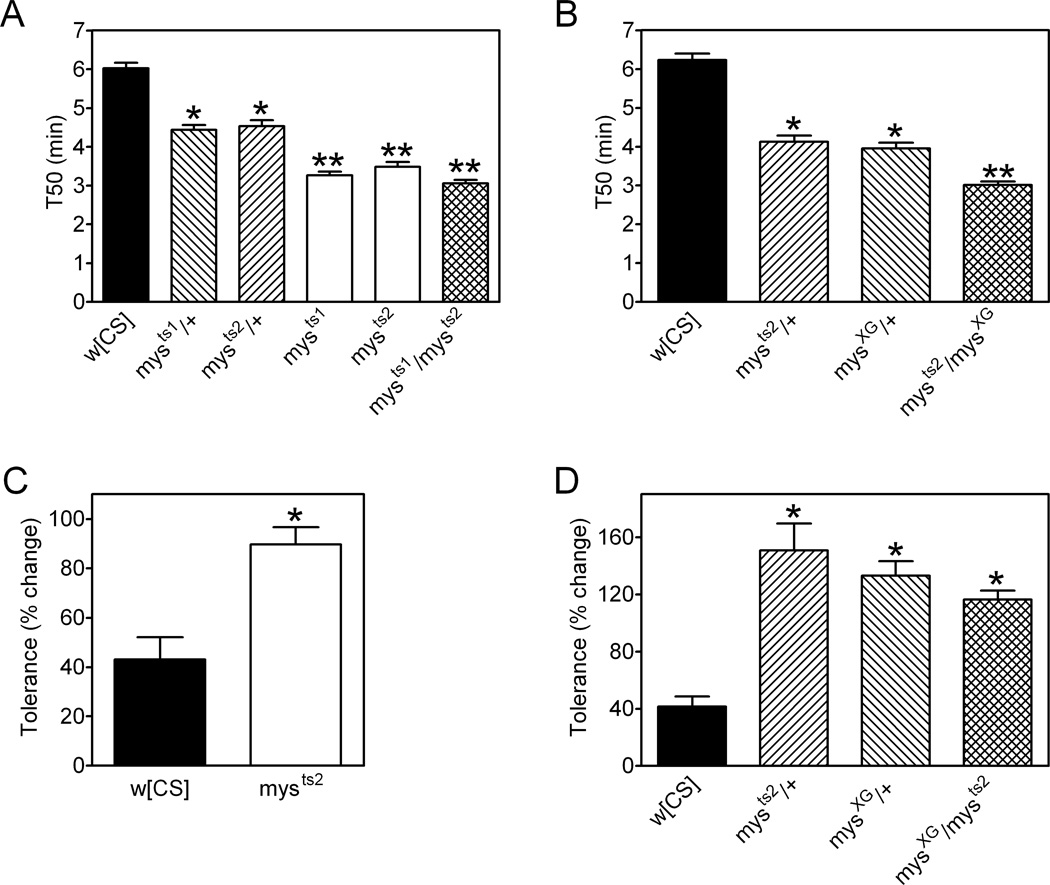
Figure 6. Ethanol sensitivity and rapid ethanol tolerance in myospheroid β integrin mutant flies.
(A and B). Ethanol sensitivity in eRING assays with vapor from a 50% ethanol solution. Overall, genotype had a significant effect on T50 values (individual one-way ANOVAs for panels A and B, p<0.0001). (A) Flies heterozygous for mysts1 or mysts2 had T50 values lower than w[CS] controls (*Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, p<0.05) and flies homozygous or transheterozygous for these two alleles had a further decrease in T50 values compared with simple heterozygous flies (**Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, p<0.05). (B) T50 values were decreased in flies heterozygous for mysXG or mysts2 compared to w[CS] controls (*Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, p<0.05) and were further decreased in flies transheterozygous for both alleles (**Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, p<0.05). (C) The development of rapid ethanol tolerance was significantly greater in mysts2 homozygous females compared to w[CS] controls (*t-test, p<0.0001). (D) Rapid ethanol tolerance was enhanced in flies heterozygous for mysXG or mysts2 as well as in transheterozygotes for these two alleles compared to control w[CS] flies (one-way ANOVA, p<0.0001, *Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, p<0.05). Data were compiled from three independent experiments for a total of 10–20 vials of 25 flies per group. All data are mean ± S.E.M.