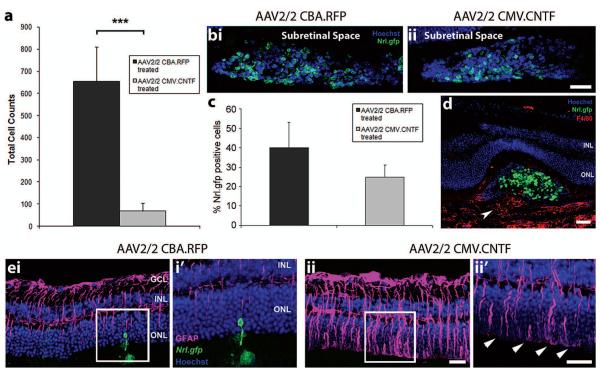
Figure 5.
The effects of secreted CNTF on transplanted photoreceptor precursors and the recipient neural retina. (a) Histogram showing the total cell counts for AAV2/2-treated eyes. A significant decrease in cell integration was observed for the AAV2/2 CMV.CNTF-treated eyes, compared to the AAV2/2 CBA.RFP-treated controls (mean ± SEM; ***p < 0.001 paired t-test; N = 9). (b,i, ii) Projection confocal images of transplanted cell masses (Nrl.gfp; green) in AAV2/2-treated eyes. (c) Histogram demonstrating the percentage of Nrl.gfp-positive cells (green) in the transplanted cell masses of AAV2/2-treated eyes (mean ± SEM; p > 0.05, paired t-test; N = 6). (d) Confocal image showing the infiltration of macrophages (F4/80, red; white arrowhead) in an AAV2/2 CMV.CNTF-treated retina. (e) Projection confocal images of retinal sections from eyes that have been transduced with AAV2/2 CBA.RFP (e,i) or AAV2/2 CMV.CNTF (e,ii), and received a subretinal cell transplantation (i′, ii′ show a single confocal image of the highlighted region). Integrated cells are present in the AAV2/2 CBA.RFP-treated retina only (ei, i′; Nrl.gfp; green). Increased GFAP was observed in the AAV2/2 CMV.CNTF-treated retina (e,ii, ii′; pink), compared to the control treated (e,i, i′). Increased staining of the glial processes at the OLM (e,ii′, white arrowheads) was present in the CNTF-treated and not the control-treated retina. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer. Scale bars: 50 μm.