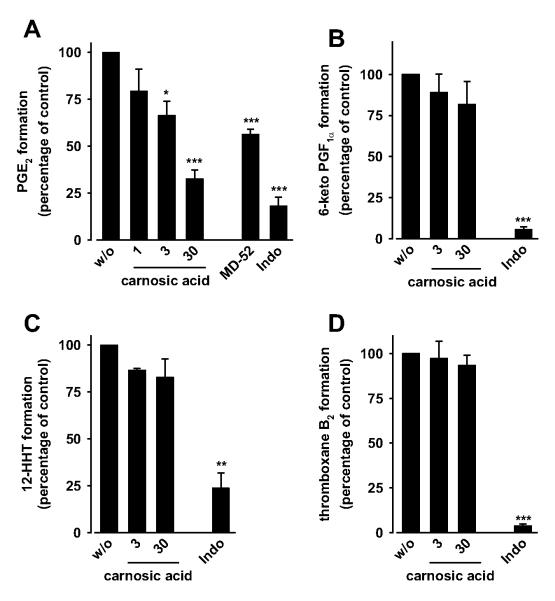
Fig. 3.
Effect of carnosol and carnosic acid on prostanoid formation in human whole blood. Aliquots of heparinized human whole blood (treated with 1 μM thromboxane synthase inhibitor and 50 μM aspirin for A and B) were preincubated with vehicle (DMSO, w/o) or carnosic acid for 5 min at room temperature, and prostanoid formation was induced by addition of 10 μg/ml LPS. Indomethacin (Indo, 10 μM) and MD52 (2 μM) were used as controls. A and C, PGE2 (A) and 12-HHT (C) were extracted from blood plasma by reversed-phase-18 solid-phase extraction, separated by reversed phase-HPLC, and quantified by ELISA (A) or UV detection (C). B and D, 6-keto PGF1α (B) and thromboxane B2 (D) were directly determined in the blood plasma by ELISA. Values of 100% correspond to 45.8 ± 5.2 ng/ml PGE2, 12.4 ± 1.6 ng/ml 6-keto PGF1α, 23.9 ± 3.2 ng/ml 12-HHT, and 67.8 ± 4.8 ng/ml thromboxane B2. Data are given as mean + S.E. (n = 1-4). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; or ***, p < 0.001 versus vehicle (DMSO) control, ANOVA + Tukey HSD post hoc tests.