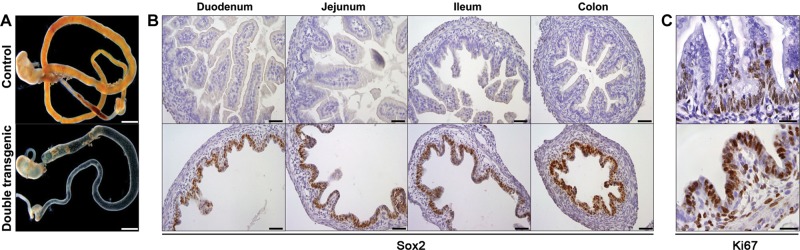
Figure 1.
Ectopic expression of Sox2 severely affects the intestinal tract. (A) Macroscopic appearances of the digestive tracts from stomach until rectum isolated at E18.5 of a non-transgenic embryo (top) and double transgenic embryo treated with doxycycline (bottom), showing that Sox2 induction leads to dilated and fluid-filled intestines. Scale bar, 2 mm. (B) IHC using an antibody against Sox2 on cross-sections of the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and colon reveals specific nuclear staining in the epithelium of double transgenic animals throughout the intestinal tract, whereas Sox2 is absent in the control. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) IHC using an antibody against Ki67 shows an increased number of cycling cells in the double transgenic embryos, compared with control intestine. Moreover, proliferating cells were randomly distributed throughout the intestinal epithelium of the double transgenic animals, whereas proliferation is restricted to the prospective crypt compartment at the base of villi in control intestines. Scale bar, 20 μm.