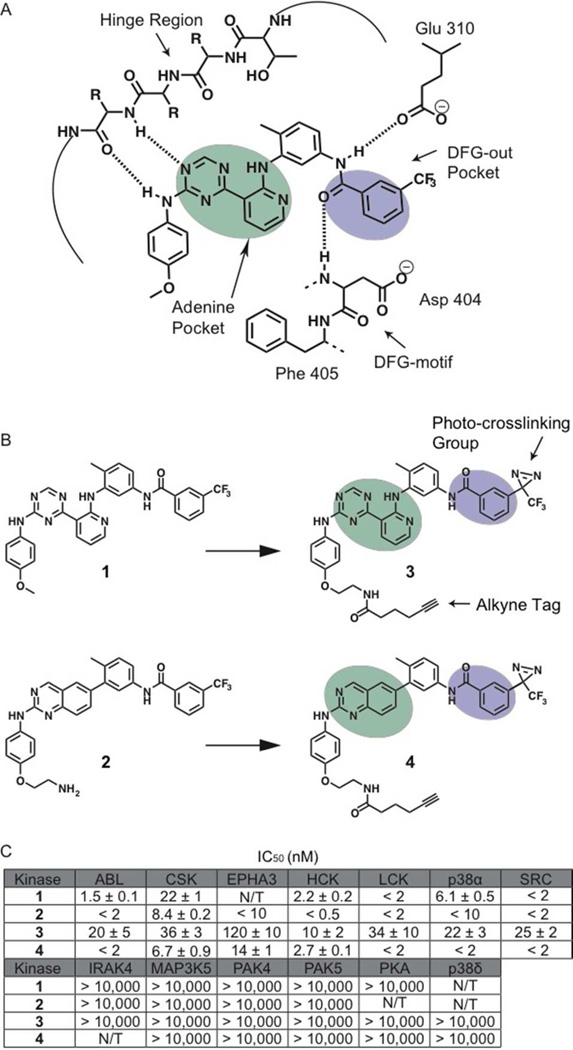
Figure 1.
Binding interactions of type II inhibitors and generation of photo-crosslinking probes. (A) A schematic representation of the interaction of type II inhibitors with the ATP-binding pocket of protein kinases. The residue numbering shown is for human c-SRC. Four hydrogen bonds are made in the binding pocket; a pair of hydrogen bonds to the hinge region, one to the conserved glutamic acid on helix-αC (Glu310) and one to the backbone of the DFG-motif. A heterocyclic moiety occupies the adenine pocket (shown in mint) while the 3-trifluoromethyl phenyl group (shown in purple) accesses the pocket (DFG-out pocket) generated by movement of the DFG-motif. (B) Chemical structures of two general type II inhibitors (1 and 2) and their corresponding probes (3 and 4) that contain a photo-crosslinking group and an alkyne tag. The 3-trifluoromethylphenyl groups (purple) of inhibitors 1 and 2 were replaced with 3-trifluoromethylphenyl diazirine moieties. In addition, the 4-anilino positions of these inhibitors were modified with alkyne tags. (C) IC50 values of 1 –4 against a panel of protein kinases. N/T = not tested. The values shown are the average of assays run in triplicate or quadruplicate +/– SEM.