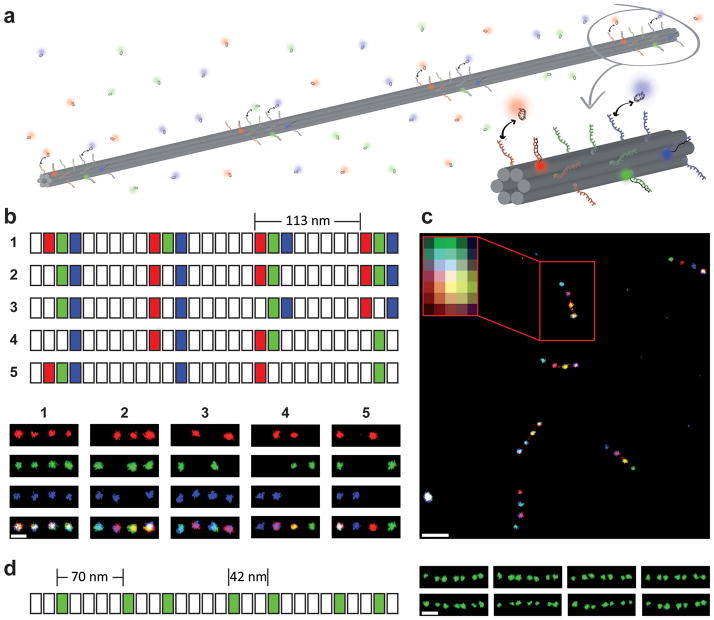
Figure 4. Super-resolution fluorescent barcodes.
(a) Schematic of barcodes for DNA-PAINT super-resolution imaging. The 400 nm DNA nanorod consists of 4 binding zones evenly spaced by ~113 nm. Each zone can be decorated with the desired combination of “docking” sequences for red, green or blue imager strands. The orthogonal imager strands bind transiently to their respective “docking” sites on the nanorod, creating the necessary “blinking” for super-resolution reconstruction. (b) Top: segment diagram (similar to Figure 1a) of the nanorod monomers used for creating five barcodes. Bottom: super-resolution images of the five barcodes shown in separate channels and as superimposed images. Scale bar: 100 nm. (c) Super-resolution image showing all five barcodes from (b) in one mixture. The inset shows the diffraction-limited image of a barcode. Scale bar: 250 nm. (d) An asymmetric barcode consisting of 7 binding zones for green imager strands spaced at ~70 nm and ~42 nm for larger and smaller distances, respectively. Scale bar: 100 nm.