Figure 2.
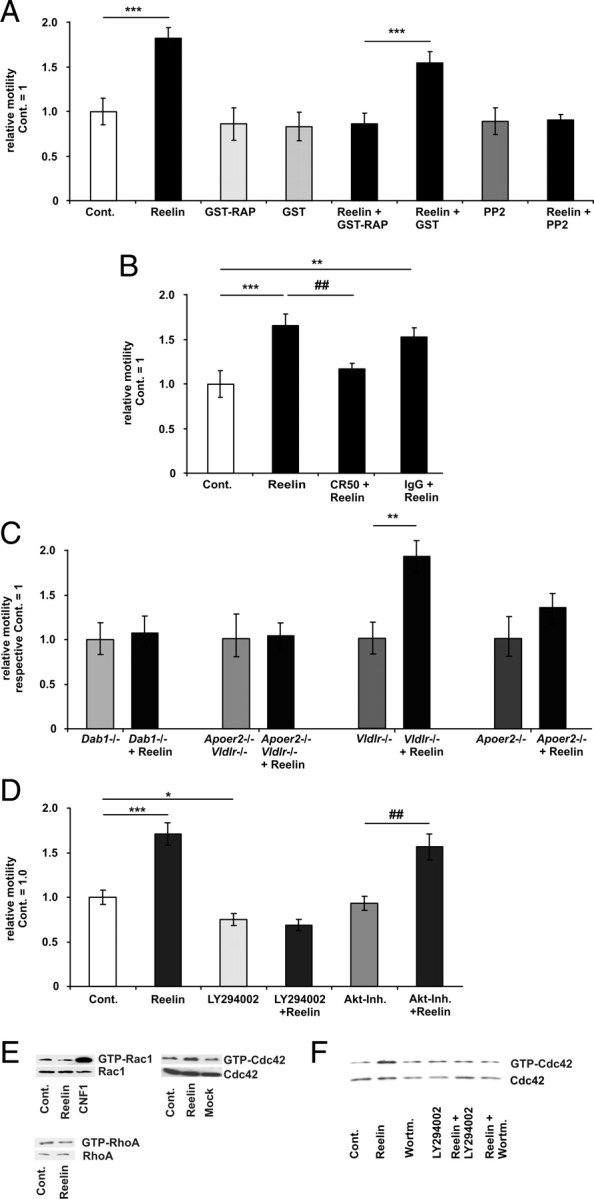
Reelin stimulates motility via Apoer2 and Cdc42. A, The motility of WT neurons was determined before and after bath application of ∼5 nm Reelin, GST-RAP, GST, Reelin, PP2, or in combination as indicated. The relative motilities of the control (Cont.) periods of each treatment group were set as 1 and were compared with the respective treatment periods. Means ± SEM; n ≥ 6; ***p < 0.001 vs control; ###p < 0.001 vs GST-RAP. B, Before the addition of Reelin, Reelin was preincubated with the Reelin-neutralizing CR-50 antibody or control mouse IgG antibody at a concentration of 200 μg/ml. Means ± SEM; n ≥ 6; ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01 vs control; ##p < 0.01 vs Reelin. C, The motility of Dab1−/−, Apoer2−/−, Vldlr−/−, and Vldlr−/− and Apoer2−/− (double knock-out) neurons was determined before and after bath application of Reelin. Means ± SEM; n ≥ 6; **p < 0.01 vs Vldlr−/−. D, The motility of WT neurons was determined before and after bath application of Reelin, LY294002, Akt inhibitor (Akt-Inh.) VIII, or in combination, as indicated (means ± SEM; n ≥ 6, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 vs controls; ##p < 0.01 vs Akt-Inh.). E, WT neurons were treated with Reelin (15 min). Afterward GTP-Rac1 or GTP-Cdc42 levels were determined by a PAK-CRIB and GTP-RhoA levels by a mDia1 pull-down assay. As a positive control for Rac activation, we applied the Rac1 activating E. coli cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 (CNF1 toxin). F, WT neurons were treated with Reelin (15 min), wortmannin (45 min), or Reelin was present during the last 15 min of wortmannin treatment (45 min). GTP-Cdc42 was determined with a PAK-CRIB pull-down assay.
