Figure 3.
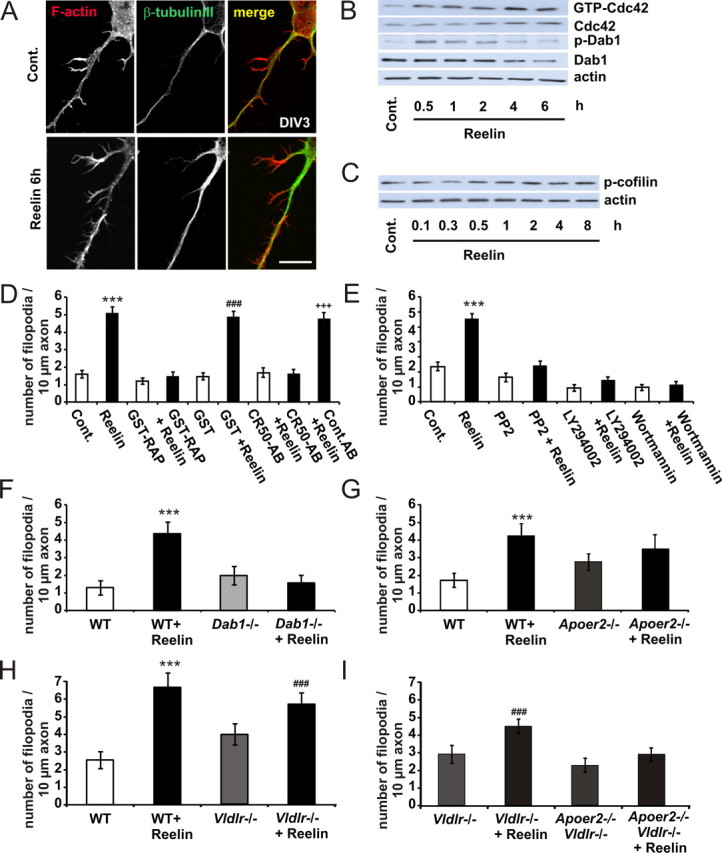
Reelin induces axonal filopodia. A, Neurons were treated with ∼0.5 nm Reelin for 6 h and stained for F-actin and β-tubulin III. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, In cortical neurons, Reelin enhanced the GTP binding of Cdc42 in a time-dependent manner, as determined by PAK-CRIB pull-down experiments. Protein levels of tyrosine-phosphorylated Dab1 detected with the anti-p-tyrosine-antibody 4G10, total Dab1, and actin in cellular lysates from control (Cont.)- or Reelin-treated neurons were measured by immunoblotting. C, Neurons were treated with Reelin for up to 8 h. Protein levels of Ser3-phosphorylated n-cofilin and actin in cellular lysates from control- or Reelin-treated neurons were measured by immunoblotting. D, E, Axonal filopodia formation of WT neurons was determined with or without bath application of Reelin, GST-RAP, GST, CR50, IgG (D), and PP2, LY294002, and wortmannin (E), or in combination, as indicated. Means ± SEM; n ≥ 30; ***p < 0.001 vs controls; ###p < 0.001 vs GST; +++p < 0.001 vs CR50-AB. F–I, Filopodia formation of Dab1−/− (F), Apoer2−/− (G), Vldlr−/− (H), and Vldlr−/−, Apoer2−/− (double knock-out; here, Vldlr−/− act as “controls” because double knock-out mice are bred on a Vldlr−/− background) (I) was determined with or without bath application of Reelin (means ± SEM; n ≥ 30; ***p < 0.001 vs WT; ###p < 0.001 vs Vldlr−/−).
