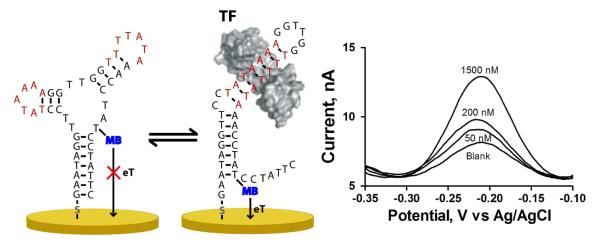
Figure 1.
The structure-switching electrochemical TF sensor is based on the use of a redox modified DNA probe, which is in equilibrium between two conformations (non-binding, left, and binding, right). Binding of the TF to its consensus sequence, shown in red, shifts the population towards binding conformation, placing the methylene blue redox tag close to the electrode surface and thus increasing its electron transfer rate (eT). Thus, in the presence of the target TF, TATA-binding protein (TBP), a robust current signal increase is observed at the redox potential characteristic of methylene blue.