Abstract
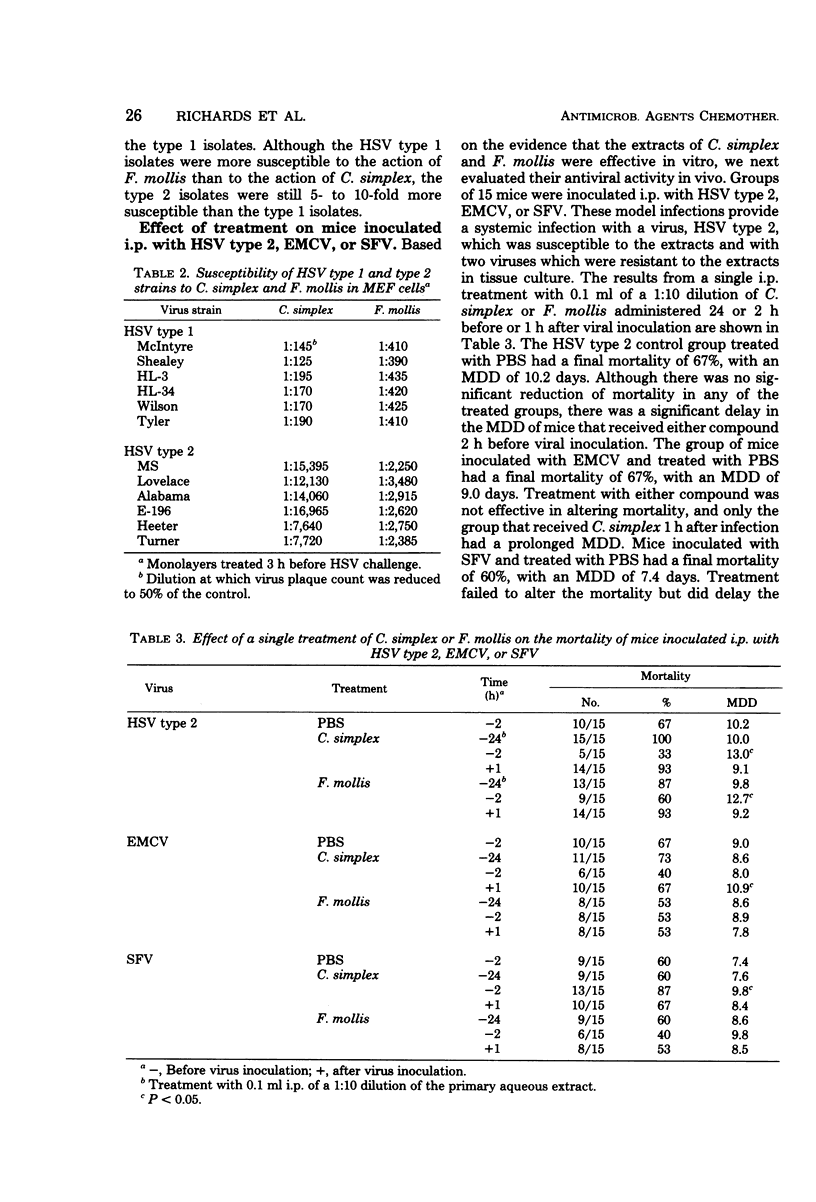
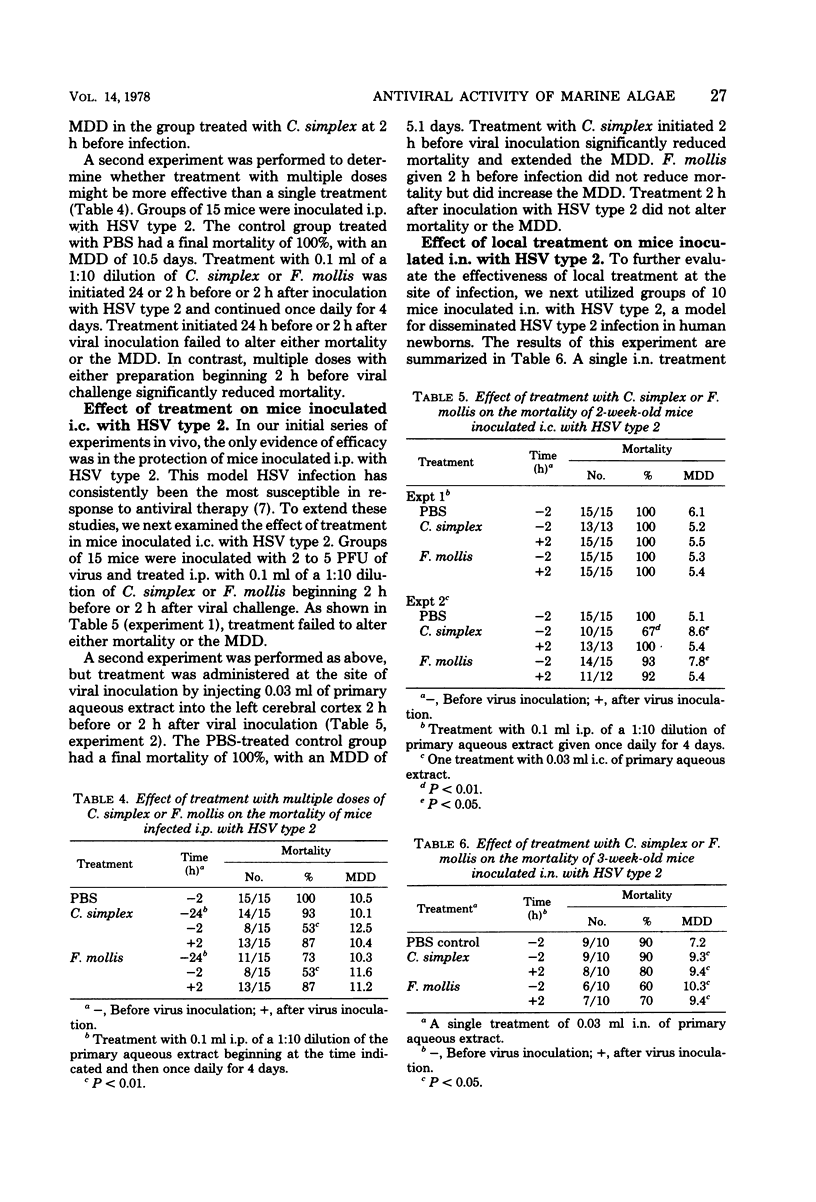
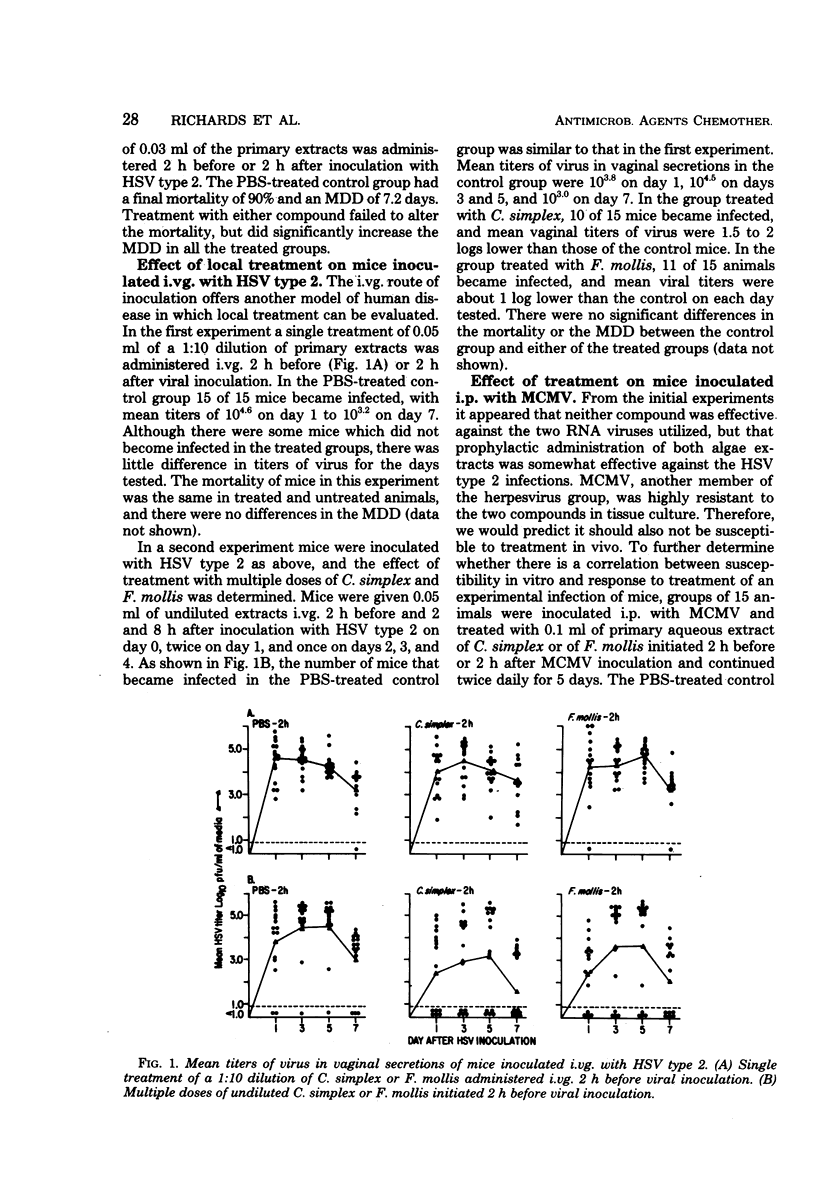
Extracts of two species of marine algae, Constantinea simplex and Farlowia mollis, were tested for antiviral activity in tissue culture and in experimental infections of mice. Treatment of confluent mouse embryo fibroblast cell monolayers with either compound before viral inoculation was effective in inhibiting the replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2, vaccinia virus, and vesicular stomatitis virus, but not encephalomyocarditis virus, Semliki Forest virus, or murine cytomegalovirus. Prophylactic administration of these extracts was effective in reducing final mortality or prolonging the mean day of death of animals inoculated by the intraperitoneal, intracerebral, or intranasal routes with herpes simplex virus type 2. When therapy was initiated after viral inoculation or at a site other than that of viral inoculation, no significant effect on mortality or on mean day of death was observed. Neither preparation was effective in mice inoculated intraperitoneally with encephalomyocarditis virus, Semliki Forest virus, or murine cytomegalovirus or in animals infected intravaginally with herpes simplex virus type 2. The prophylactic but not therapeutic antiviral activity of these preparations seriously limits their potential use in human herpes simplex virus infections.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deig E. F., Ehresmann D. W., Hatch M. T., Riedlinger D. J. Inhibition of herpesvirus replication by marine algae extracts. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Oct;6(4):524–525. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.4.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Hamilton J. R., Overall J. C., Glasgow L. A. Antiviral activity of BL-3849A, a low-molecular-weight oral interferon inducer. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 Oct;10(4):691–696. doi: 10.1128/aac.10.4.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Herpesvirus hominis infection in newborn mice. I. An experimental model and therapy with iododeoxyuridine. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):290–299. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Richards J. T., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Alteration of mortality and pathogenesis of three experimental Herpesvirus hominis infections of mice with adenine arabinoside 5'-monophosphate, adenine arabinoside, and phosphonoacetic acid. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1978 Jan;13(1):53–60. doi: 10.1128/aac.13.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern E. R., Richards J. T., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Genital Herpesvirus homonis infection in mice. II. Treatment with phosphonoacetic acid, adenine arabinoside, and adenine arabinoside 5'-monophosphate. J Infect Dis. 1977 Apr;135(4):557–567. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.4.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overall J. C., Jr, Kern E. R., Schlitzer R. L., Friedman S. B., Glasgow L. A. Genital herpesvirus hominis infection in mice. I. Development of an experimental model. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):476–480. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.476-480.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow D. A., Overall J. C., Jr, Glasgow L. A. Interferon inducers in therapy of infection with encephalomyocarditis virus in mice. I. Effect of single doses of polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidylic acid and tilorone hydrochloride on viral pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130(5):470–480. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.5.470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


