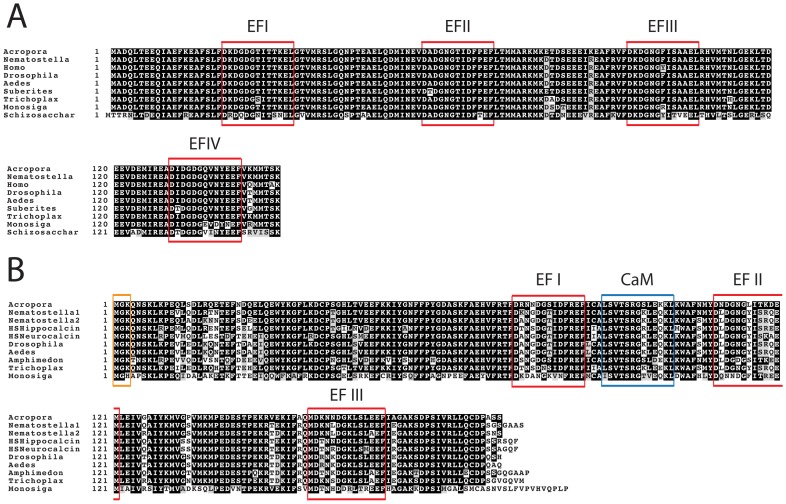
Figure 1. Primary structure of the coral EF-hand proteins.
(A) As in the canonical calmodulins of a wide range of other eukaryotes, the AmCaM protein contains four predicted EF-hand motifs, each of which fulfils the criteria for activity. Genbank identifiers for the sequences: Acropora Cluster 043479; Nematostella XP_00163858.1; Homo NP_001734.1; Drosophila NP_523710.1; Aedes XP_001662431.1; Suberites O97341; Trichoplax EDV29861.1; Monosiga XP_001749021.1; Schizosaccharomyces XP_002175972. (B) The coral Acrocalcin (AmAC) protein is a typical member of the NCS-B class, possessing an N-terminal myristoylation site (MGK, orange box), three EF-hand motifs (indicated by red boxes) and a predicted CaM-binding site (blue box). Genbank identifiers for sequences: Acropora Cluster 013002; Nematostella1 XP_001639634.1; Nematostella2 XP_001639635.1; HS (Homo sapiens) hippocalcin NP_002140.2; HS (Homo sapiens) neurocalcin NP_114430; Drosophila NP_788543.1; Aedes XP_001648788.1; Amphimedon XP_003386697.1; Trichoplax EDV23214.1; Monosiga EDQ90181.1.