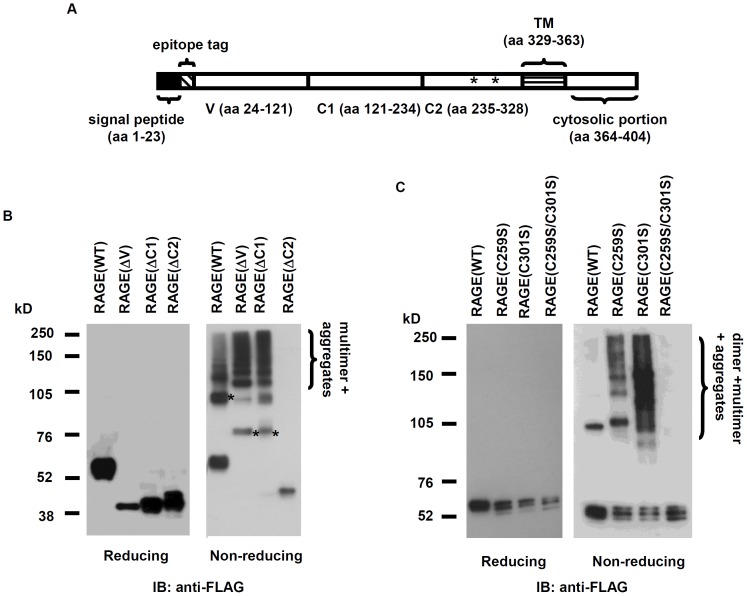
Figure 2. Intermolecular disulfide bonds contribute to the formation of RAGE dimers.
(A) Schematic drawing of RAGE domains. aa: amino acids; * indicates C259 and C301; TM: transmembrane helix. (B) Identification of RAGE domain that is responsible for covalent-linked dimerization. About 5 µg of total membrane extracts was loaded. * indicate dimers of RAGE (WT) and deletion mutants. (C) RAGe C2 domain exhibits disulfide bond-mediated dimerization. * indicate dimers of RAGE(WT) and RAGE(C2). (D) Testing whether C259 and C301 are responsible for covalent-linked dimerization of RAGE. About 7.5 µg of total membrane extracts was loaded.