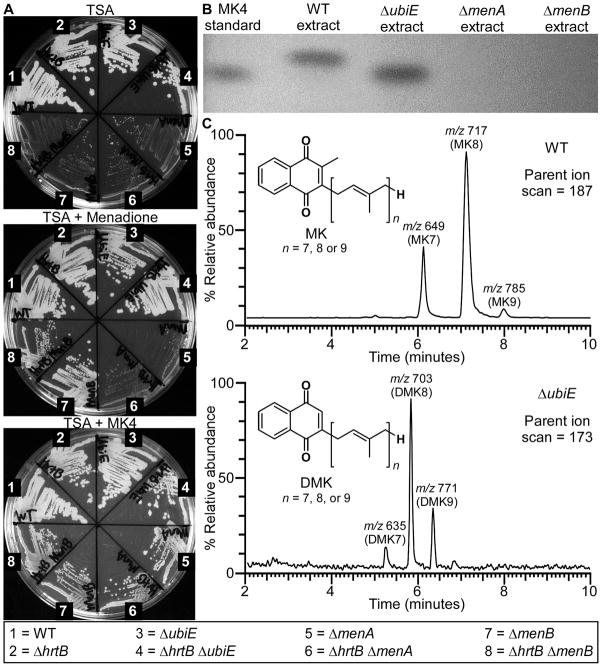
Fig. 2. Non-polar deletions of the final enzymatic steps of the S. aureus MK biosynthesis pathway can be generated and chemically characterized.
A. WT and various mutants of S. aureus were plated on agar to highlight differences in colony morphology for certain strains when grown on plain TSA medium versus growth in the presence of 12.5 μM exogenous menaquinone-4 (MK4) or 2.5 μM of the MK precursor, menadione. Pictures were taken after 48 hours of growth at 37 °C. B. MK and DMK were extracted from various S. aureus strains, resolved by thin layer chromatography (TLC) adjacent to a commercially available MK standard (MK4), and visualized by UV shadowing. C. MK and DMK extracts isolated from the WT and ΔubiE S. aureus strains were further resolved by mass spectrometry, revealing the number of isoprenyl groups (highlighted by brackets in the inset chemical structures) present on each of these molecules. MK and DMK were detected using parent ion scans for m/z 187 and m/z 173, respectively as previously described (Geyer et al., 2004).