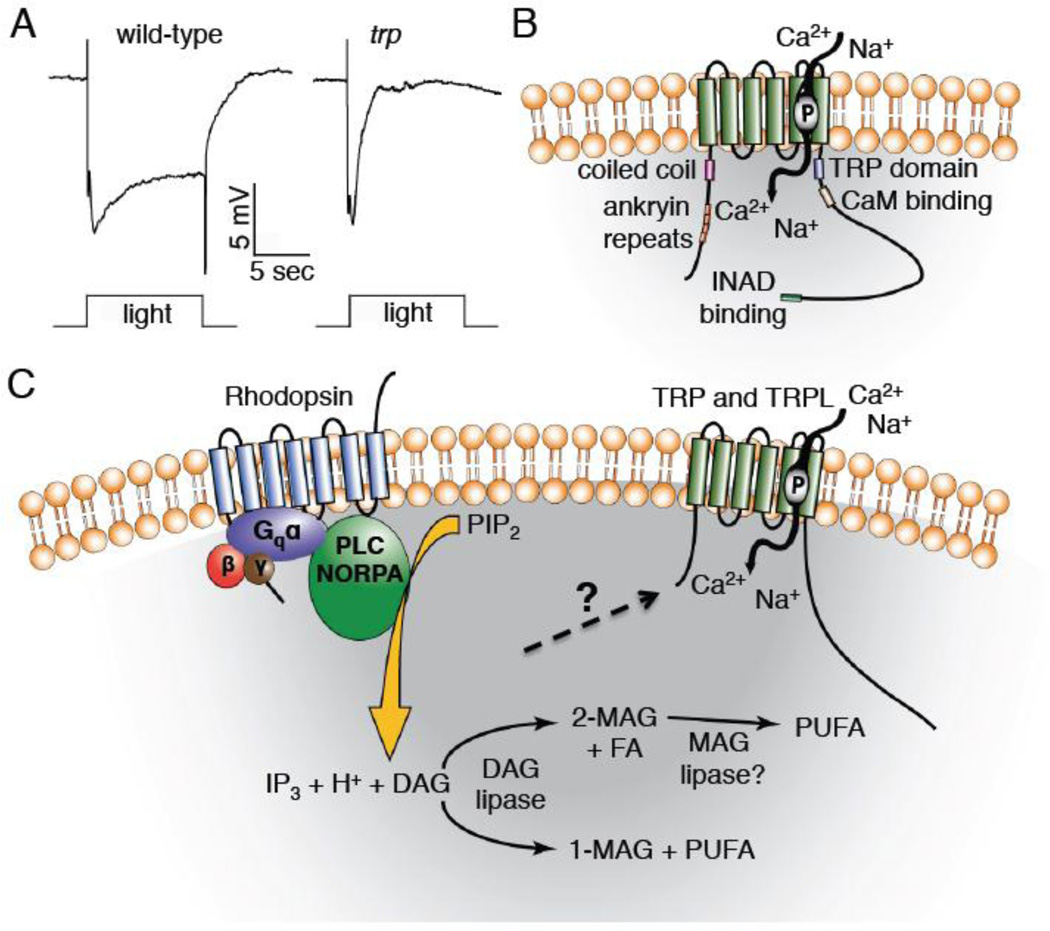
Figure 2. Predicted TRP structure and the phototransduction that leads to activation of TRP and TRPL.
A) Electroretinogram (ERG) recordings from trp+ (w1118) and trp343 mutant flies (performed by Dr. Zijing Chen). B) Predicted structure of the Drosophila TRP channel. The channel contains six transmembrane domains, with the pore loop located between the 5th and 6th transmembrane domains. The N-terminal region contains four ankyrin repeat domains and a coiled coil domain, and the C-terminal tail contains a TRP domain, calmodulin (CaM) binding site, and an INAD binding site. C) Model of Drosophila phototransduction. Light capture by rhodopsin initiates a Gq/PLC signaling cascade that culminates in activation of the TRP and TRPL channels and influx of cations. Abbreviations: 1-MAG, monoacylglycerol; 2-MAG, 2-monoacylglycerol; DAG, diacylglycerol; FA, saturated fatty acid; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; MAG, monoacylglycerol; P, pore loop indicated in TRP; PUFA, polyunsaturated fatty acid.