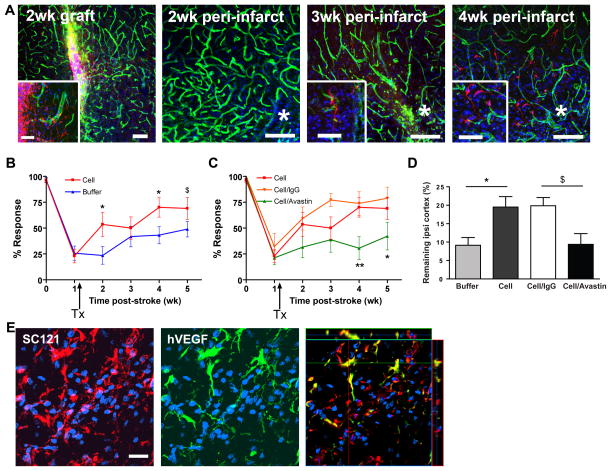
Figure 1. hCNS-SCns enhance functional recovery and reduce cortical atrophy in a hVEGF-dependent manner.
(A) hCNS-SCns (red: human cytoplasmic marker SC121) survive and migrate over time; green: lectin-positive blood vessels; blue: DAPI. * indicates lesion. Inset: higher magnification of hCNS-SCns. Scale: 100μm (50μm in inset, except 3 wk inset: 25μm). (B) hCNS-SCns-treated animals (n=10) showed significantly improved behavioral recovery after stroke compared to buffer-treated animals (n=14). TX: transplantation. P=0.032 by repeated measures ANOVA; * p<0.05; $ p=0.06 by t-test. (C) Avastin treatment significantly blocked hCNS-SCns-induced recovery. p=0.02 by repeated measures ANOVA between cell/Avastin and cell groups; * p<0.05; ** p<0.01 by t-test; cell/Avastin: n= 12–9; cell/IgG: n=7–4, (wk (0–3) - wk (4–5)). (D) The volume of the remaining ipsilesional cortex was significantly larger in hCNS-SCns-treated versus buffer-treated animals at 4 wk post-transplantation; this effect was blocked by Avastin. * p<0.05 by t-test; $ p=0.06 by Mann-Whitney; n=4–5. (E) hCNS-SCns (red) express hVEGF (green). The anti-VEGF antibody is specific for human VEGF and does not cross react with rat VEGF Scale: 50μm.