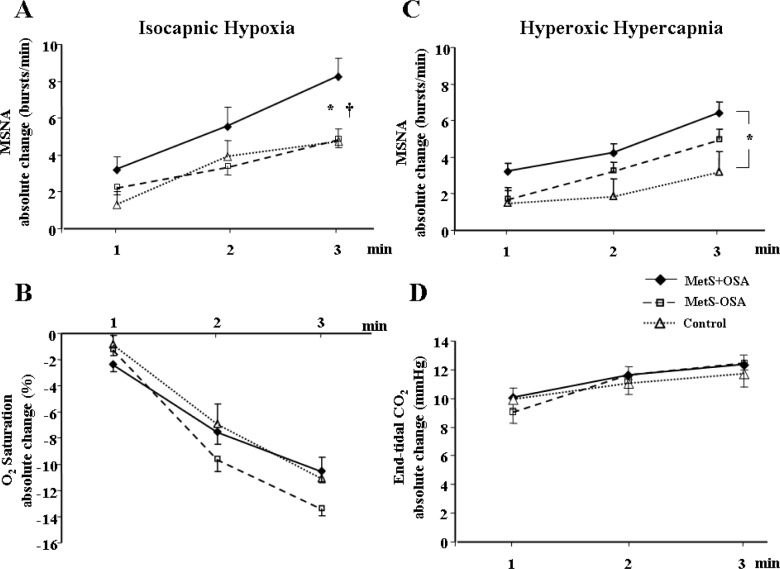
Figure 2.
(A) Absolute change of muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA) and (B) oxygen saturation (O2 saturation) during isocapnic hypoxia and (C) absolute change of MSNA and (D) carbon dioxide exhaled (End-tidal CO2) during hyperoxic hypercapnia in patients with metabolic syndrome plus obstructive sleep apnea (MetS + OSA), patients with metabolic syndrome without obstructive sleep apnea (MetS – OSA) and normal control subjects. Note that, either during isocapnic hypoxia or during hyperoxic hypercapnia, MetS + OSA group had higher MSNA responses than control subjects. In addition, during isocapnic hypoxia MetS + OSA patients have higher MSNA responses compared with MetS – OSA patients. *P < 0.05 versus control; †P < 0.05 versus MetS – OSA.