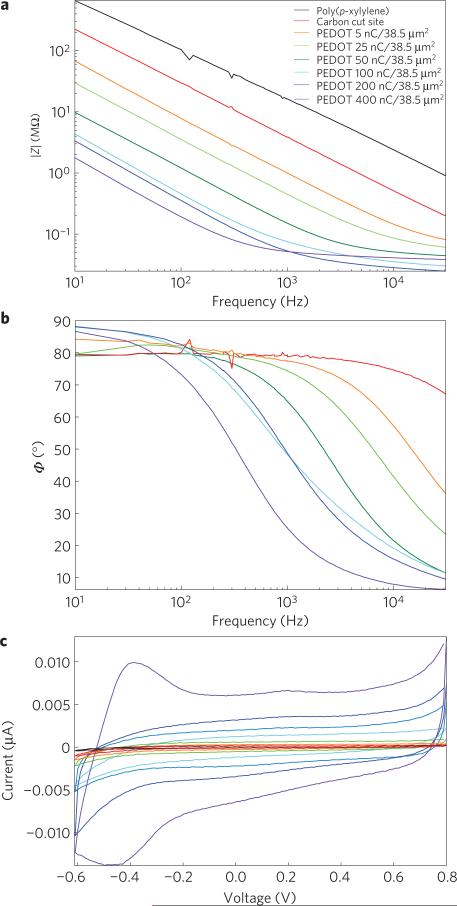
Figure 2. In vitro electrical characterization of MTEs.
a,b, Electrical characterization of a poly(p-xylylene)-coated carbon fibre, a poly(p-xylylene)-coated fibre with an exposed carbon tip and a poly(p-xylylene)-coated fibre with a recording site of PEDOT:PSS electrodeposited with applied charges of 5, 25, 50, 100, 200 and 400 nC. a, Bode magnitude impedance plot showing decreasing impedance with increasing PEDOT deposition across all frequencies. b, Bode phase plot showing phase shift towards smaller phases indicative of a change from a capacitive carbon interface to a faradaic PEDOT interface with increasing deposition. The poly(p-xylylene)-insulated fibre without an exposed recording site was not plotted because a reliable signal could not be detected. c, Cyclic voltammogram showing increasing charge storage capacity with increasing PEDOT deposition in response to voltage cycling of the electrode site.