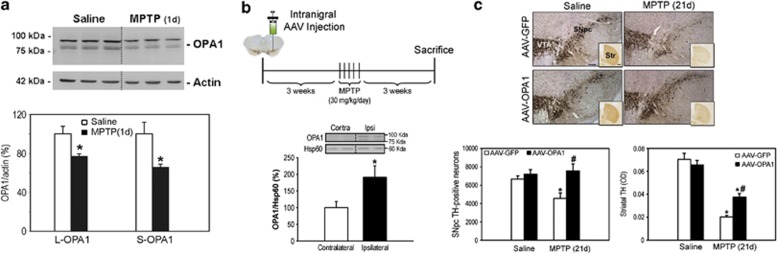
Figure 5.
OPA1 overexpression attenuates dopaminergic nigrostriatal denervation in MPTP-intoxicated mice. (a) OPA1 immunoblot levels (L-OPA1, ∼100 kDa; S-OPA1, ∼80 kDa) by SDS-PAGE in ventral midbrain samples from mice treated with either saline or MPTP (30 mg/kg per day for 5 consecutive days) and killed 24 h (1 day) after the last saline or MPTP injection. (b) Schematic representation of the experimental design used for AAV-OPA1 injections in MPTP-treated mice (top). OPA1 immunoblot levels in mouse ventral midbrain samples ipsilateral and contralateral to AAV-OPA1 injections (bottom). (c) Representative photomicrographs of TH-immunostained SNpc (brown; thionin in purple) and striatum (Str, inset) from saline- and MPTP-treated mice, overexpressing GFP or OPA1, at day 21 post MPTP (top). Stereological cell counts of SNpc TH-immunoreactive neurons (left) and optical densitometry of striatal TH immunoreactivity (right) in the different experimental groups of animals at day 21 post MPTP (bottom). Histograms represent average±S.E.M. (n=5–8 animals per group); *P<0.05 compared with saline-injected mice; #P<0.05 compared with MPTP-treated GFP-expressing mice; Scale bar, 500 mM