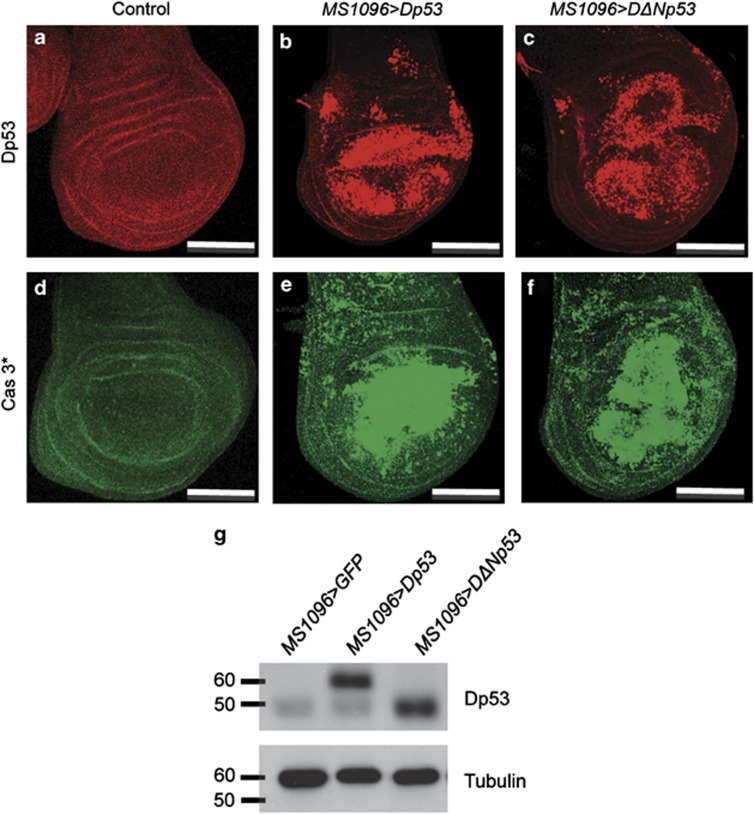
Figure 1.
Dp53 or DΔNp53 expression induces caspase activation in wing imaginal discs. (a–f) Ectopic production of Dp53 or DΔNp53 using the MS1096 driver. (a–c) Dp53 and DΔNp53 protein isoforms are detected by immunostaining with an anti-p53 antibody (25F4) directed against the common C terminus domain. (a) MS1096>GFP is used as a negative control. Dp53 (b) and DΔNp53 (c) are detected in the MS1096 domain of expression. (d–f) Wing imaginal discs were stained using an anti-cleaved caspase 3 antibody (Cas 3*). Elevated levels of Dp53 (MS1096>Dp53 in e) or DΔNp53 (MS1096>DΔNp53 in f) induce strong caspase 3 staining in the MS1096 domain. Caspase activation is not detected in control wing discs (MS1096>LacZ in d). (g) Western blot analysis of Dp53 and DΔNp53 in the wing imaginal discs using an anti-p53 antibody (C11) against the common C terminus domain. MS1096>Dp53 and MS1096>DΔNp53 show a band around 60 kDa and 50 kDa, respectively. The endogenous level of DΔNp53 is detected in the wild-type control (MS1096>GFP). Tubulin is used as loading control. Scale bars are 100 μm