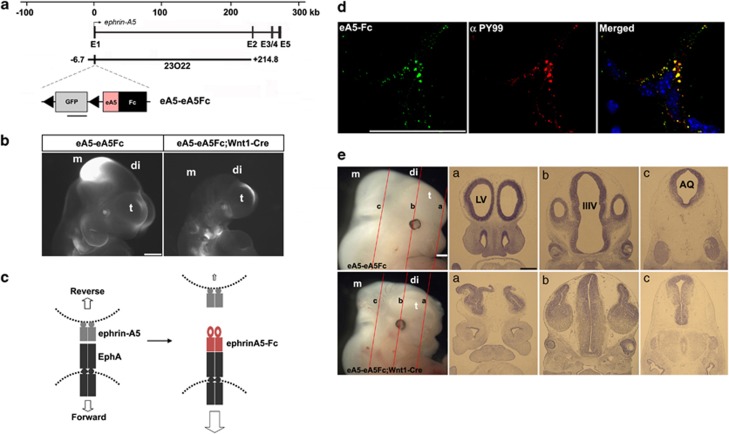
Figure 3.
Severe brain malformation in mouse embryos expressing ephrin-A5-Fc. (a) Schematic map of the ephrin-A5 genomic locus with the ephrin-A5 BAC clone (RP23-23O22). The modified ephrin-A5 BAC clone, eA5-eA5Fc, is identical to the original ephrin-A5 BAC clone, except that it contains a floxed GFP followed by an ephrin-A5-Fc expression cassette inserted upstream into the translation start codon in the first exon of ephrin-A5. (b) GFP fluorescent image of the indicated transgenic embryo at E10.5. GFP images were compared after littermate embryos were obtained from crossing eA5-eA5Fc BAC transgenic mice with Wnt1-Cre mice. Three different transgenic lines were generated with the same result. (c) Schematic diagram showing that soluble ephrin-A5-Fc is secreted from ephrin-A5-expressing cells and that they bind to and activate EphA receptors in the neighboring NECs. (d) In vitro-dissociated NECs were cultured and treated with soluble ephrin-A5-Fc (unclustered) for 30 min at 37°C. Cells were fixed and immunostained using anti-phosphotyrosine antibody (αPY99) and anti-human IgG conjugated to Alexa488. (e) Comparison of E12.5 littermate embryos from a cross between eA5-eA5Fc BAC transgenic mice and Wnt1-Cre mice. Similar results were consistently observed in three different transgenic lines when each line was mated with Wnt1-Cre mice. (a–c) Coronal sections corresponding to each line shown in E12.5 embryos were stained using cresyl violet. t, telencephalon; di, diencephalon; m, mesencephalon; LV, lateral ventricle; IIIV, third ventricle; AQ, cerebral aqueduct. Scale bars=500 μm (b, e) and 50 μm (d)