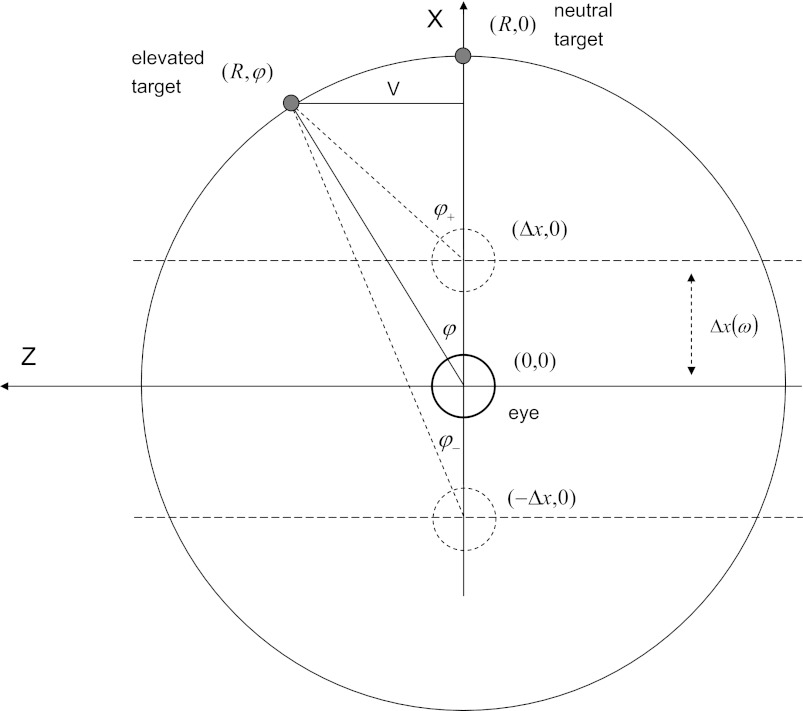
Fig. 1.
Geometry of the isovergence gaze targets. Subject is supine with head to the left. Eye positions relative to the targets are indicated by small circles. Dashed circles show eye positions at maximum displacement. Viewing distance is given by the radius R of the array. Vertical gaze eccentricity V is determined by the vertical resting gaze angle φ. Linear displacement Δx is a function of stimulus frequency.