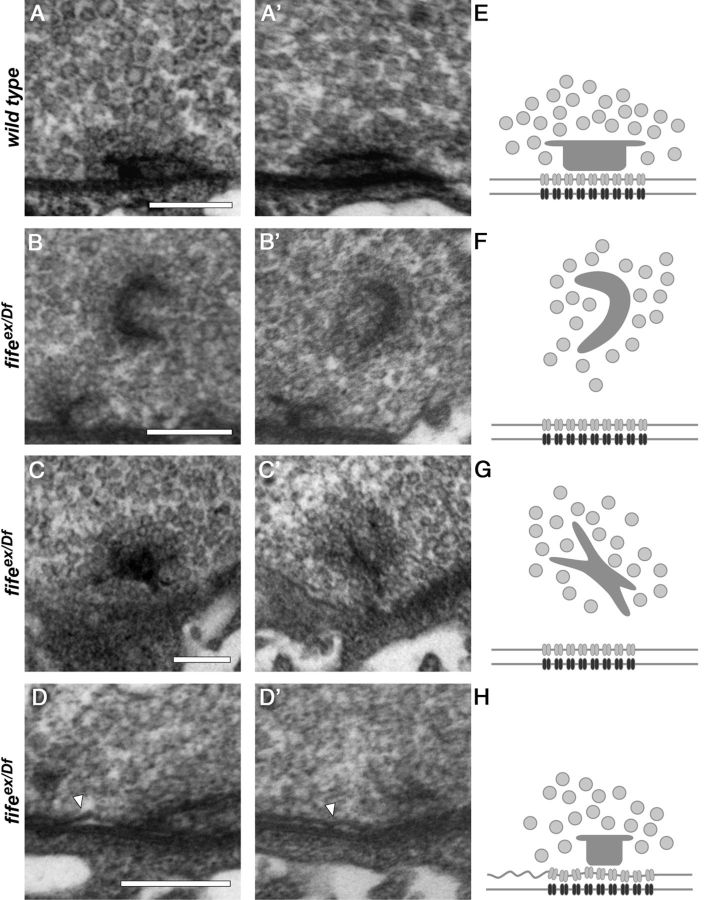
Figure 6.
Fife is required for normal active zone architecture. A–D′, Representative transmission electron micrographs of serial sections of wild-type (A, A′) and fifeex/Df (fifeex1027/Df (3L) BSC412) (B–D′) synapses. A, A′, Two serial sections of a wild-type synapse reveal a platform-shaped electron-dense projection (T-bar) that clusters synaptic vesicles at the presynaptic membrane. Tight apposition of the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is maintained across the length of synapse. B, B′, Two serial sections of a fifeex/Df synapse reveal an ectopic, electron-dense structure distant from the presynaptic membrane. This T-bar-like malformation still maintains local clustering of synaptic vesicles. C, C′, A second example of an ectopic electron density in two serial sections of a fifeex/Df synapse. D, D′, Two serial sections of a typical fifeex/Df synapse demonstrate loss of the close apposition of presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes in fife mutants (arrowhead). E–H, Schematic representations of the AZs and ectopic densities depicted in A–D′ including synaptic vesicles (light gray circles), T-bars (dark gray structures), calcium channels (gray), and postsynaptic receptors (black). Scale bars, 200 nm.