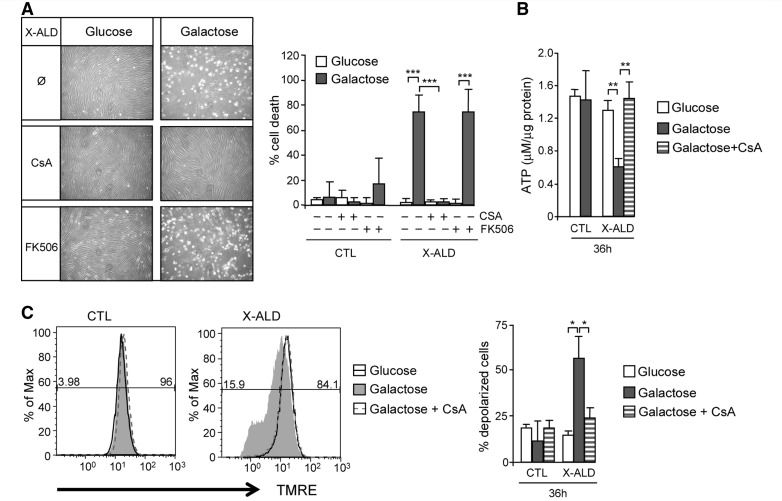
Figure 5.
Galactose-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy fibroblasts is caused by mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening. Control and X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy fibroblasts cultured in glucose or galactose were treated with 5 µM of cyclosporin A or 5 µM of FK506, and cell death was measured (A). In the same conditions with cyclosporin A treatment, ATP content (B) and inner mitochondrial membrane potential (C) were quantified (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; n = 4/genotype and condition). In C, the numeric values above the line correspond to the percentage of polarized cells on the right-hand and depolarized cells on the left-hand of each panel. CsA = cyclosporin A; CTL = control; X-ALD = X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.