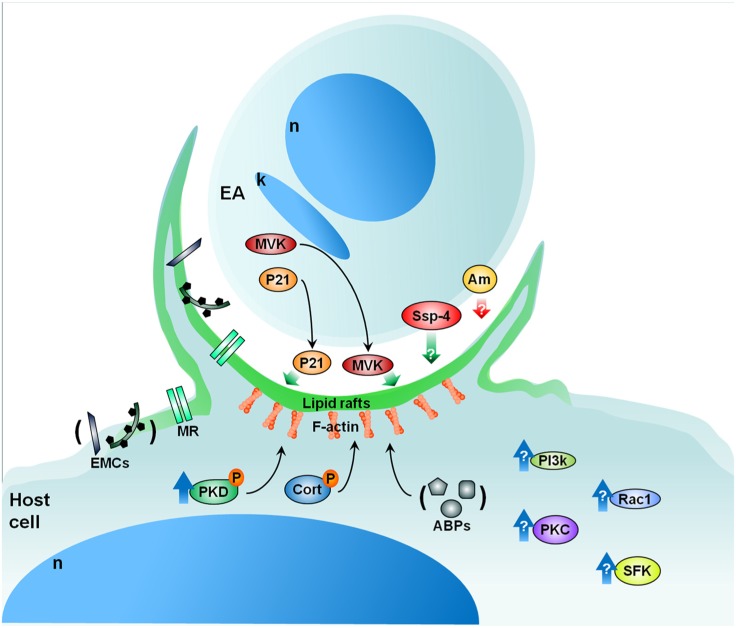
FIGURE 3.
Proposed model for EA signaling. EAs secrete factors such as P21 and MVK that aid in EA uptake by cells in culture. EAs also present specific glycoproteins (i.e., Ssp-4) important for attachment and penetration while other EA glycoproteins (i.e., amastins-Am) may negatively modulate amastigote invasion. From the cellular perspective, lipid rafts are essential to parasite internalization in both macrophages and epithelial cells. Furthermore, the mannose receptor of certain cells may recognize mannose residues expressed by EAs which also participate in EA uptake. Upon contact, EAs recruit PKD, actin (F-actin), and other actin-binding proteins (ABPs) such as cortactin (Cort), gelsolin, and α-actinin. Additionally, EAs likely activate Src-family kinase (SFK), PKC, and Rac1 signaling in host cells. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases (PI3k) pathway may also be involved in EA internalization. Cellular heparan sulfate and fibronectin are also important in the process of EA internalization (extracellular matrix components – ECMs). Red and green arrows: negative and positive modulation of the invasion, respectively; blue arrows: host protein activation; black arrows: recruitment. P, phosphorylation; n, nucleus; k, kinetoplast; MVK, mevalonate kinase; MR, mannose receptor. See text for more details.