Figure 1.
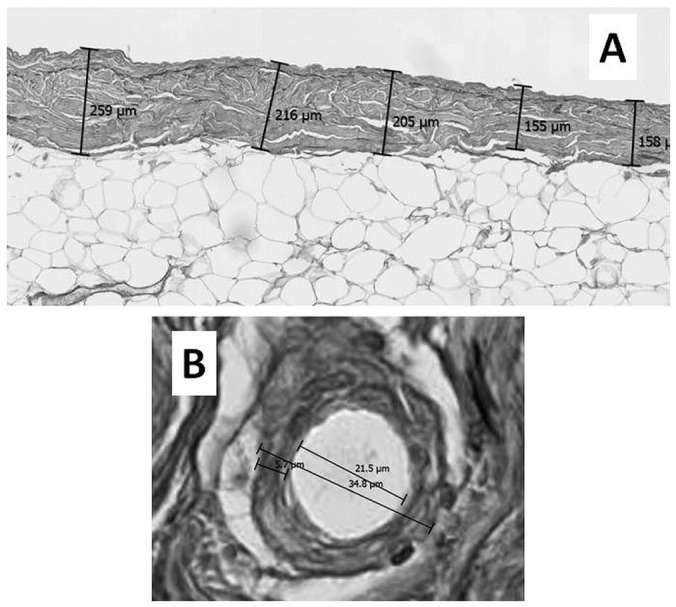
— Evaluation methods for peritoneal sclerosis. (A) Average peritoneal thickness (APT) by the 5-point measurement method. Peritoneal thickness is measured at 5 randomly selected points, and the APT is then calculated. In this peritoneal dialysis patient (number 10), peritoneal thicknesses ranged from 155 μm to 259 μm. The APT was calculated to be 198.6 μm. The average of 2 APT values determined by 2 examiners was taken as the representative APT for this patient. (B) Quantitative evaluation of vasculopathy at a postcapillary venule (PCV). Severity of luminal narrowing was determined using the ratio of luminal diameter to vessel diameter (L/V), representing the patency of the blood vessel. A PCV whose diameter was in the range 25 – 50 μm was selected for measurement. The short axis was measured, with the most severely affected vessel being chosen for the measurement. The average of 2 L/V values determined by 2 examiners was taken as the representative L/V. In this peritoneal dialysis patient (number 8), the luminal and vessel diameters were 21.5 μm and 34.8 μm respectively. Thus, the final L/V ratio was 0.62.
